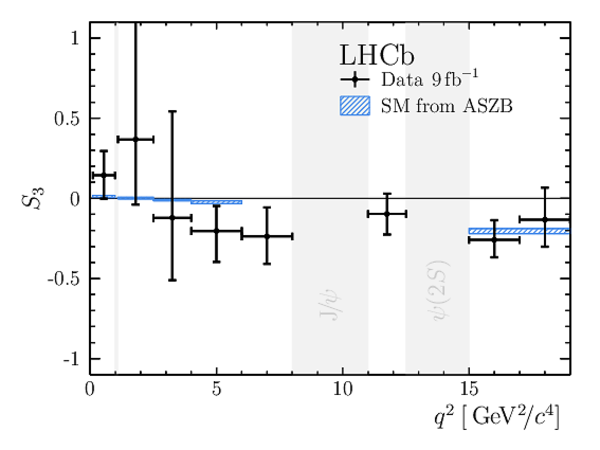
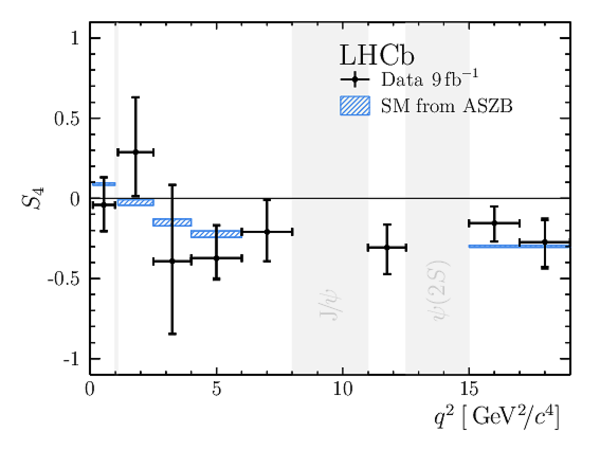
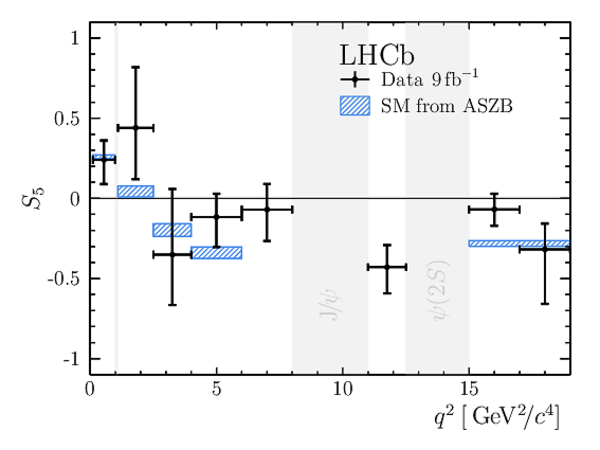
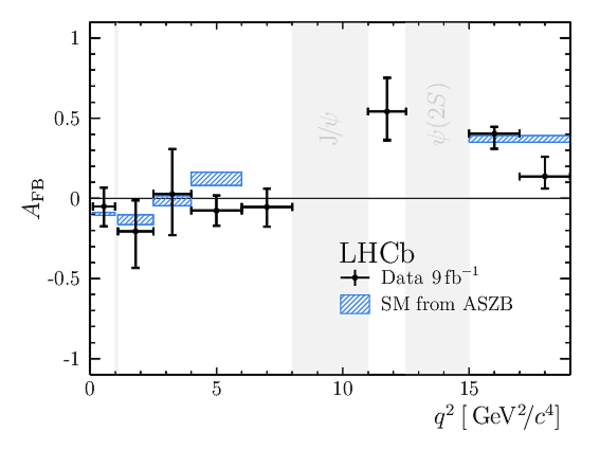
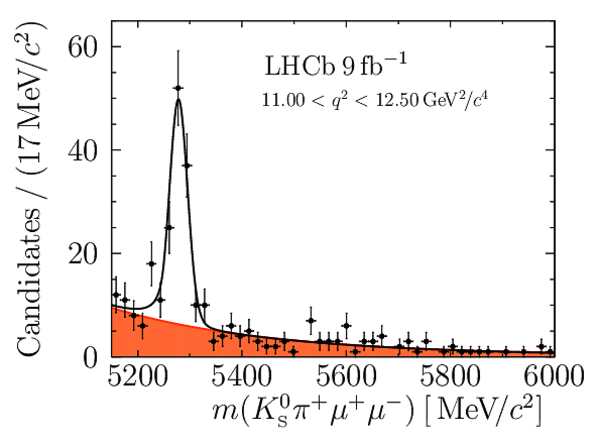
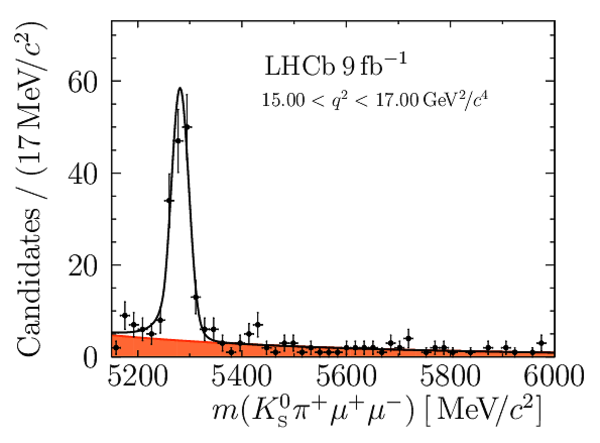
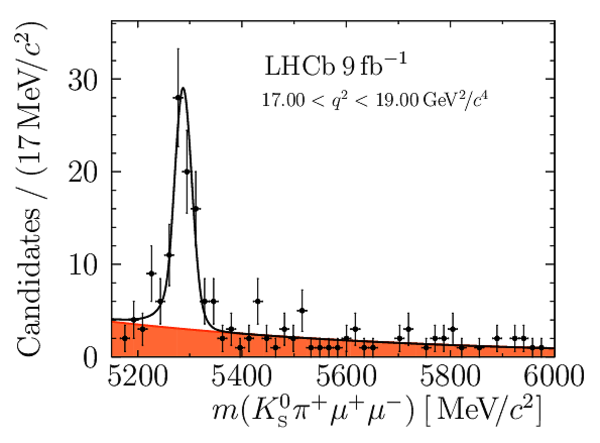
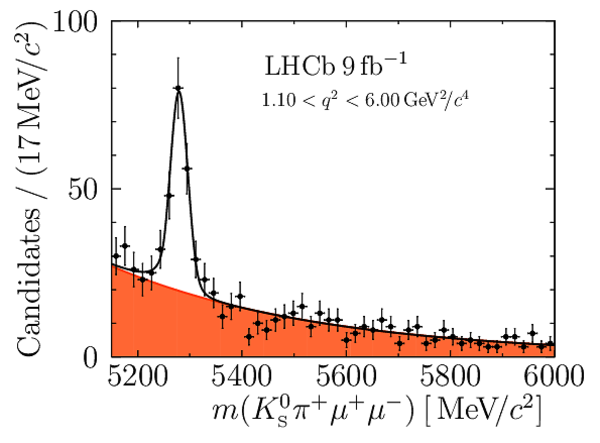
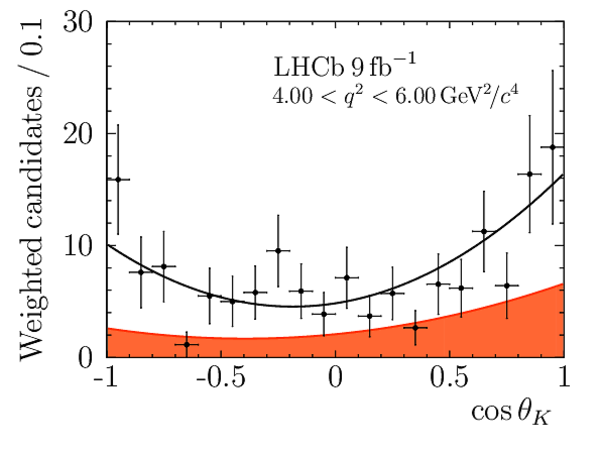
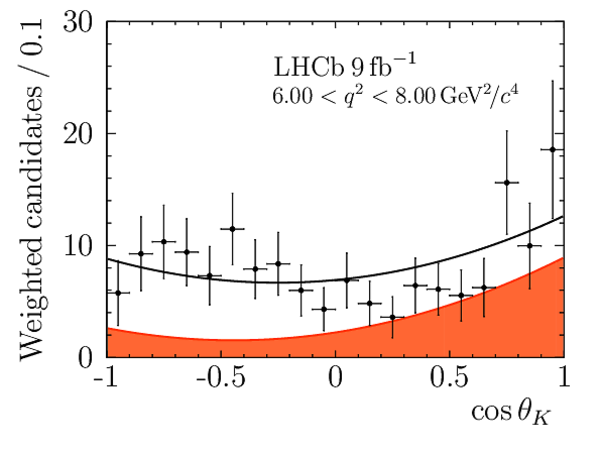
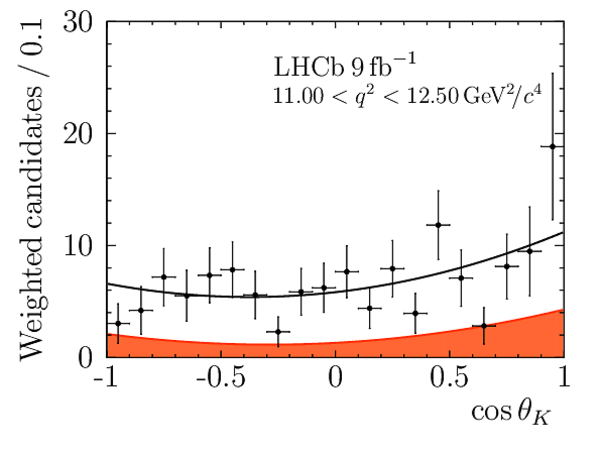
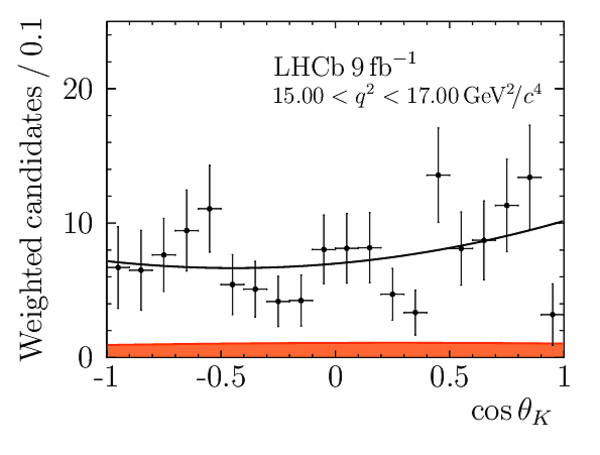
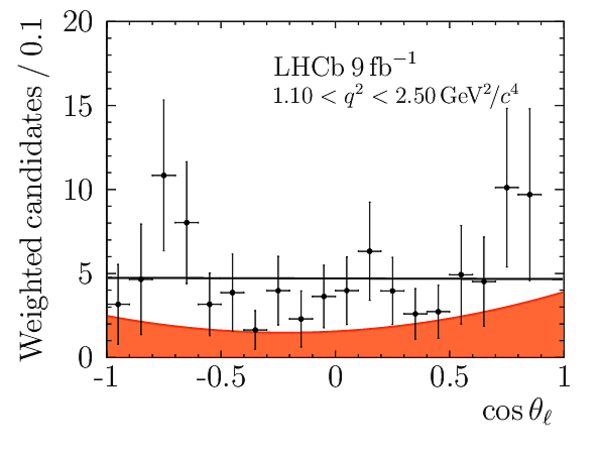
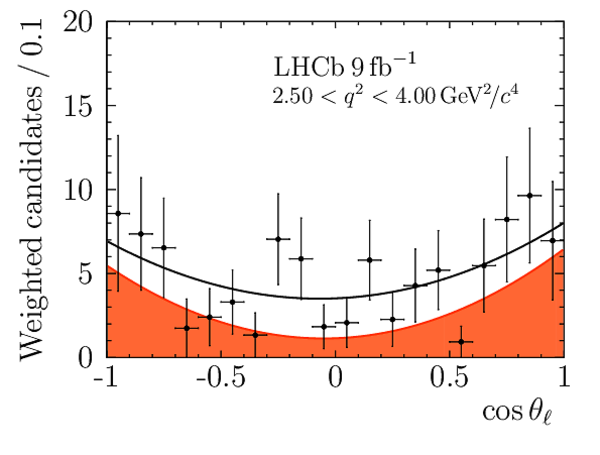
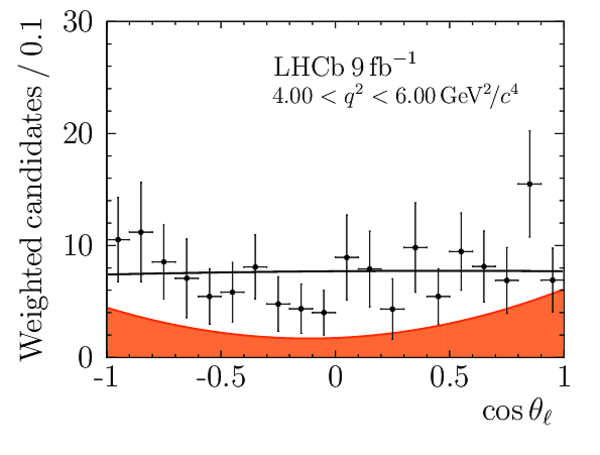
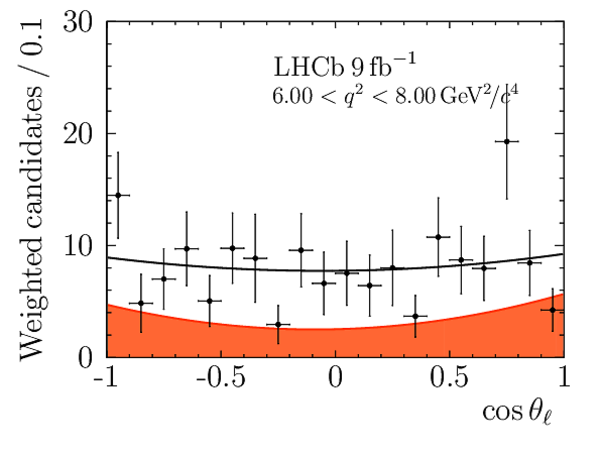
Angular Analysis of the $B^{+}\rightarrow K^{\ast+}\mu^{+}\mu^{-}$ Decay
[to restricted-access page]Information
LHCb-PAPER-2020-041
CERN-EP-2020-239
arXiv:2012.13241 [PDF]
(Submitted on 24 Dec 2020)
Phys. Rev. Lett.126 (2021) 161802
Inspire 1838196
Tools
Abstract
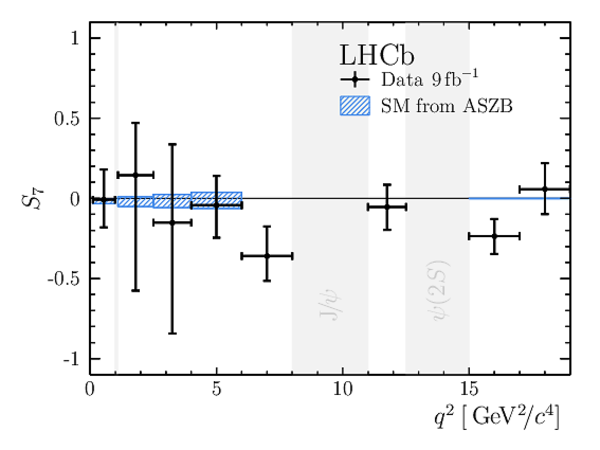
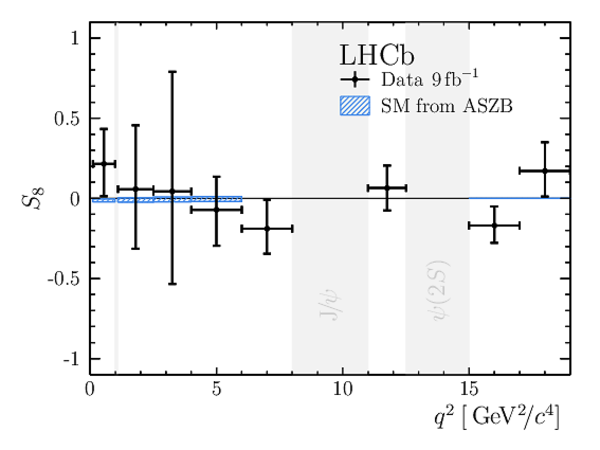
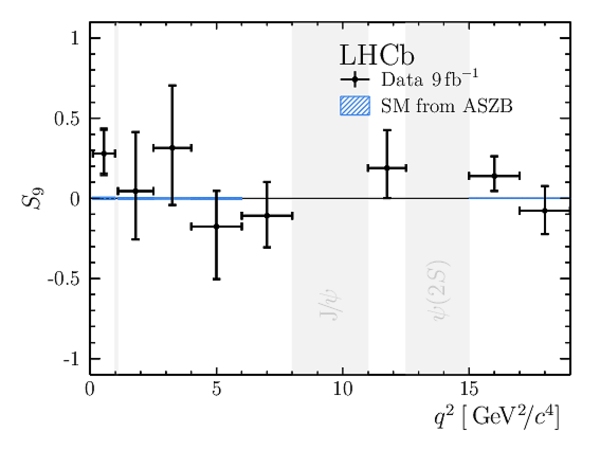
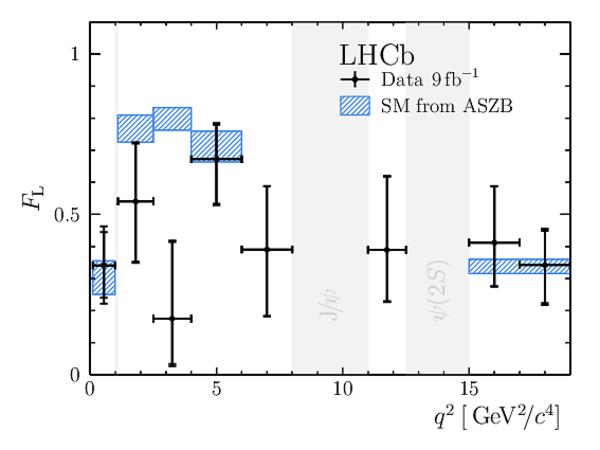
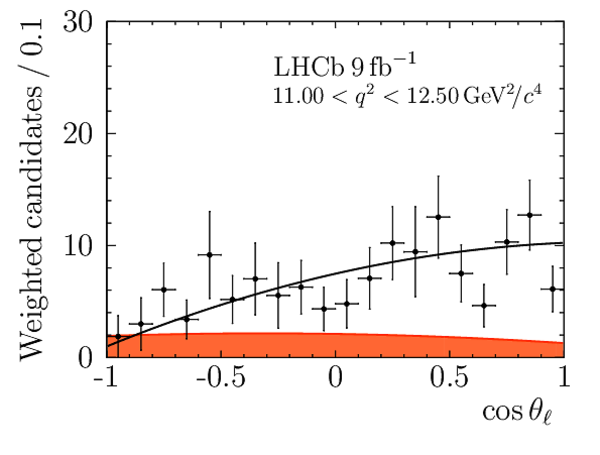
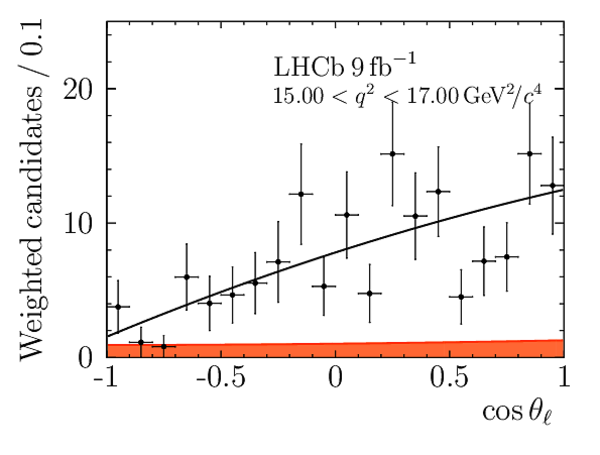
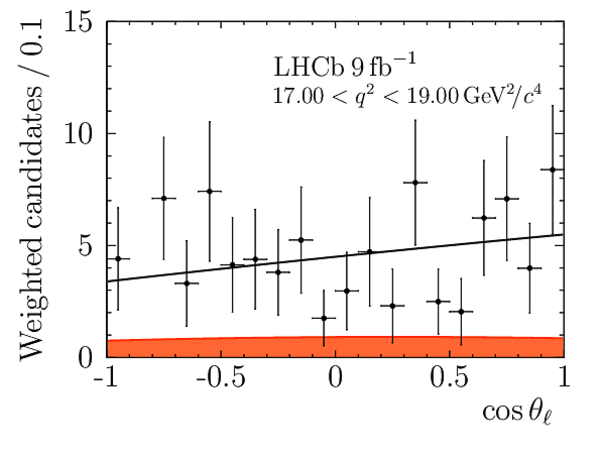
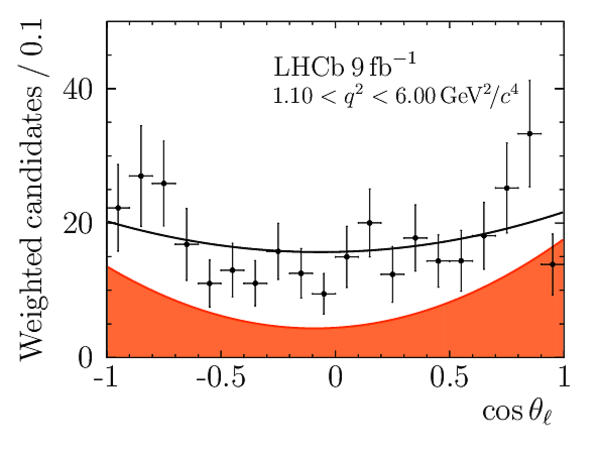
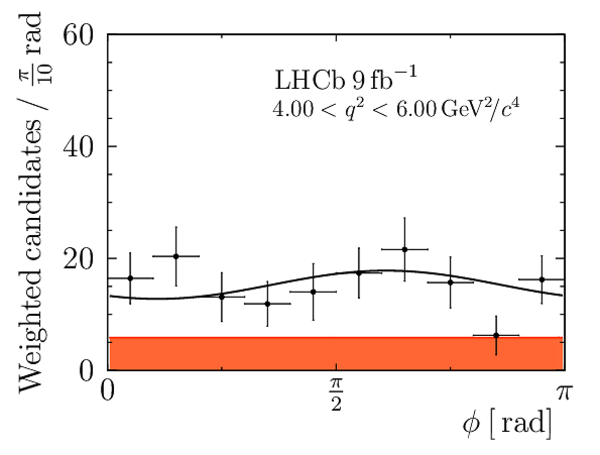
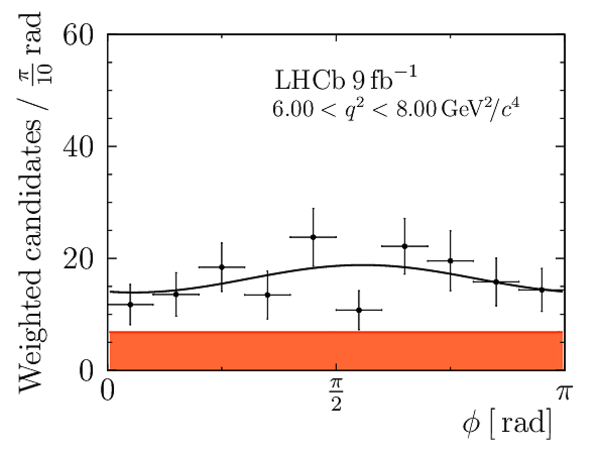
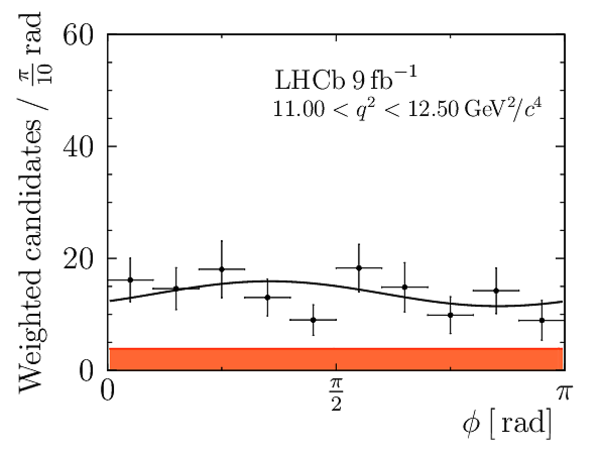
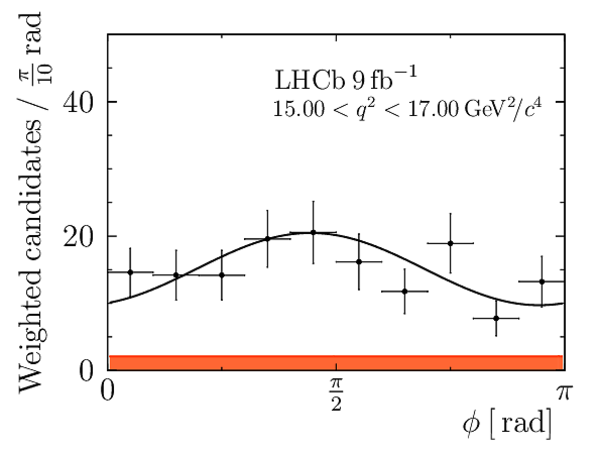
We present an angular analysis of the $B^{+}\rightarrow K^{\ast+}(\rightarrow K_{S}^{0}\pi^{+})\mu^{+}\mu^{-}$ decay using 9$ fb^{-1}$ of $pp$ collision data collected with the LHCb experiment. For the first time, the full set of CP-averaged angular observables is measured in intervals of the dimuon invariant mass squared. Local deviations from Standard Model predictions are observed, similar to those in previous LHCb analyses of the isospin-partner $B^{0}\rightarrow K^{\ast0}\mu^{+}\mu^{-}$ decay. The global tension is dependent on which effective couplings are considered and on the choice of theory nuisance parameters.
Figures and captions
Tables and captions
|
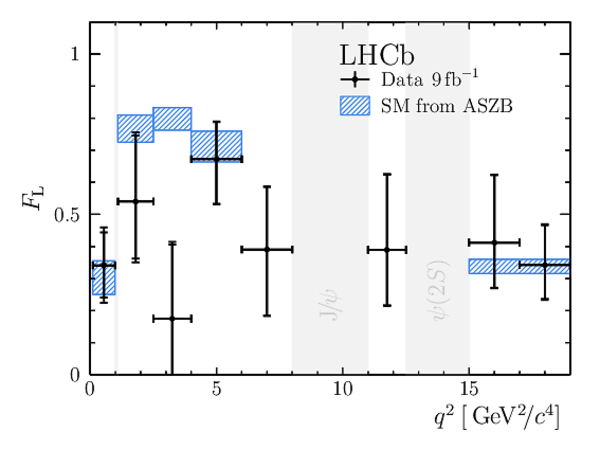
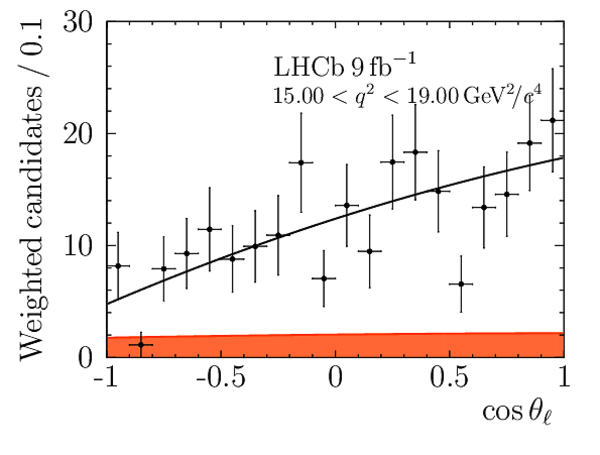
Results for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$. The first uncertainties are statistical and the second systematic. |
[Error creating the table] | |
|
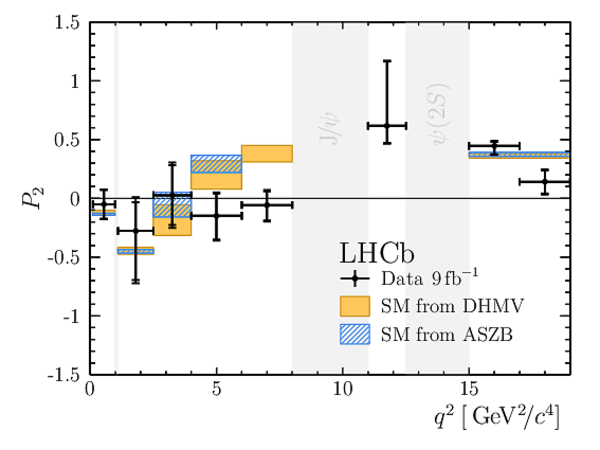
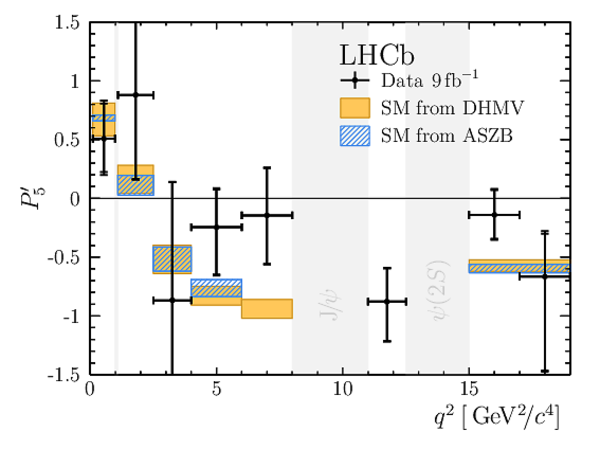
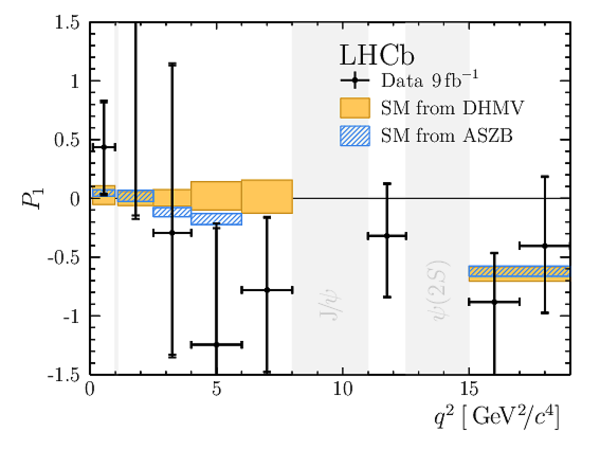
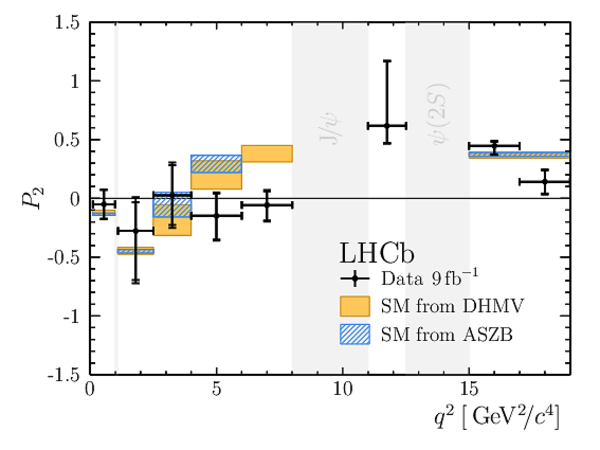
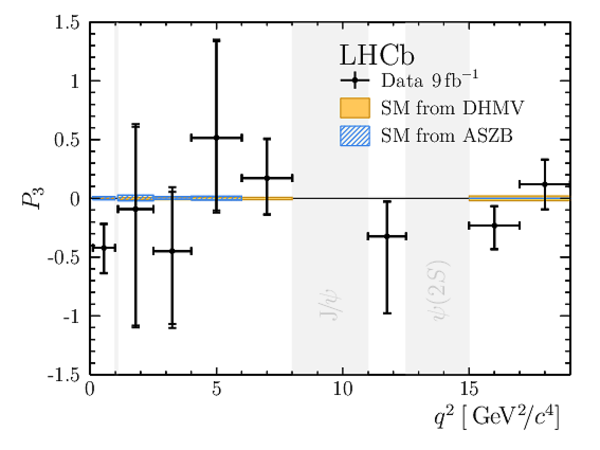
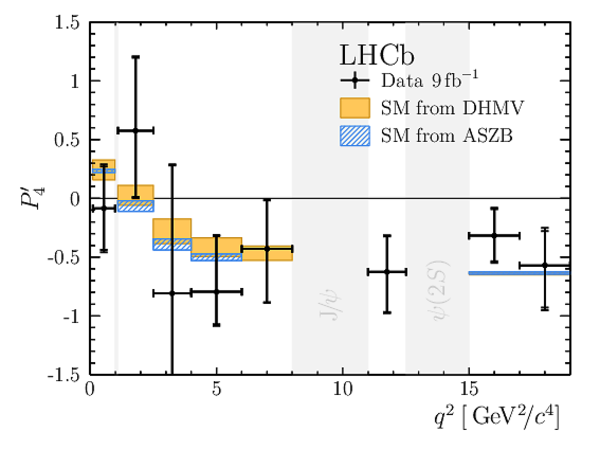
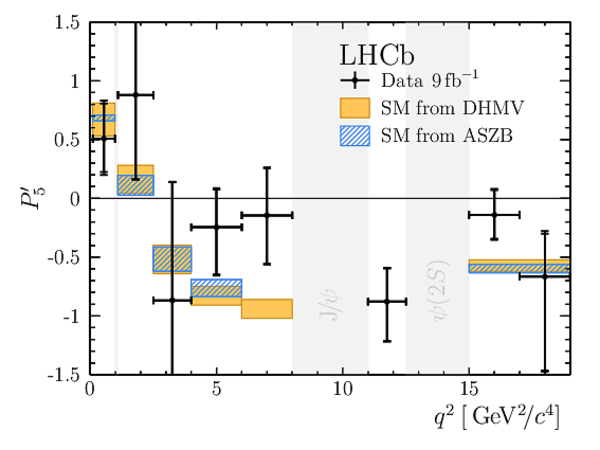
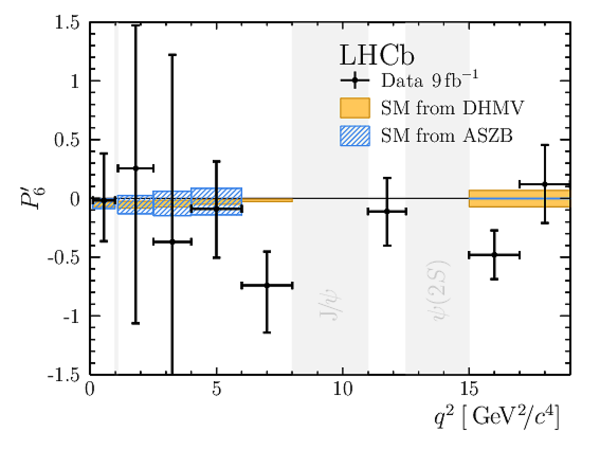
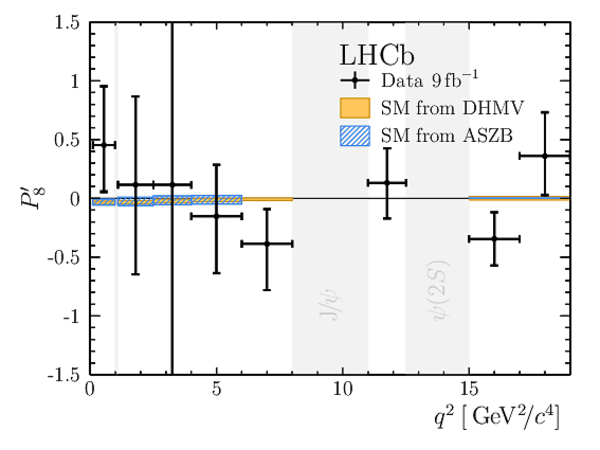
Results for the optimised observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_1\text{--}P_8^{\prime}$. The first uncertainties are statistical and the second systematic. |
[Error creating the table] | |
|
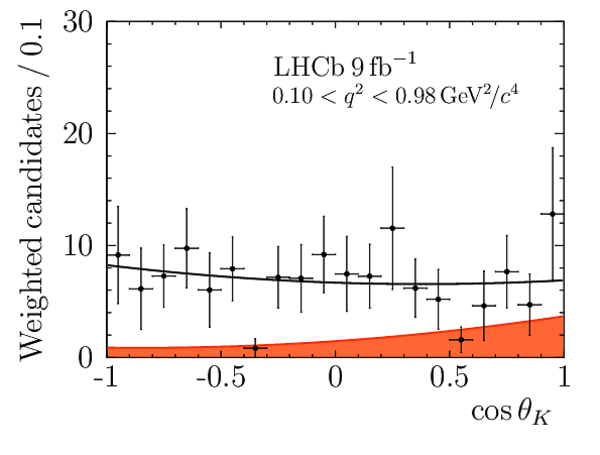
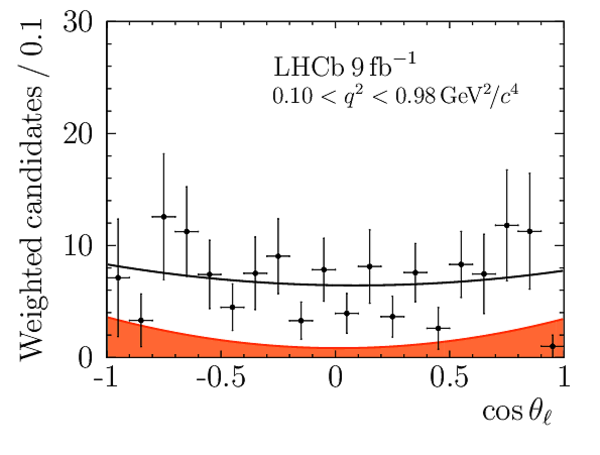
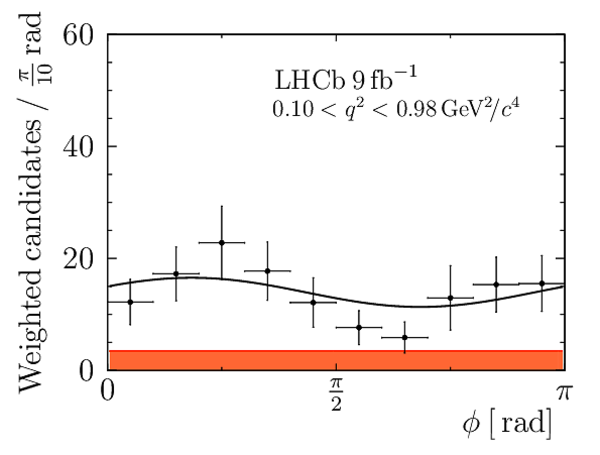
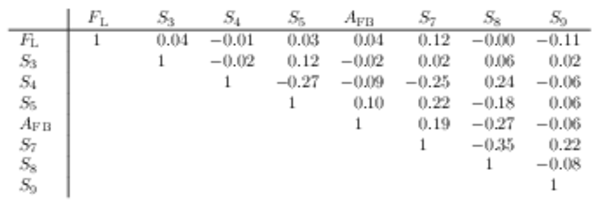
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $0.10< q^2 <0.98\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_3.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
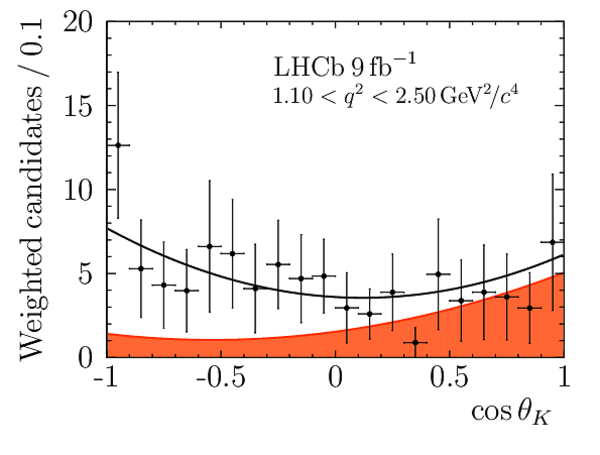
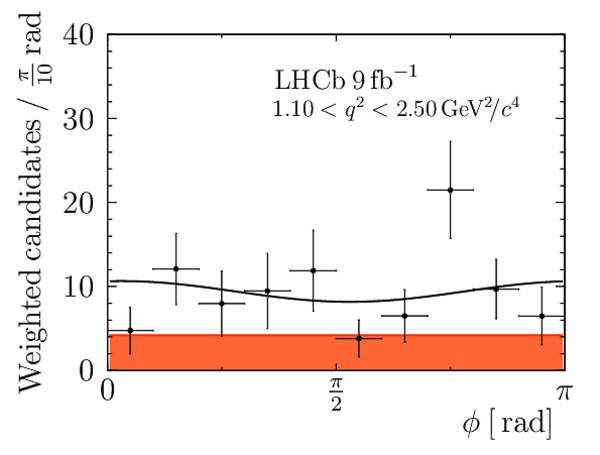
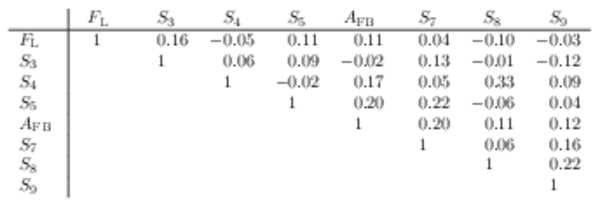
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $1.1< q^2 <2.5\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_4.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [44 KiB] Thumbnail [20 KiB] tex code |
|
|
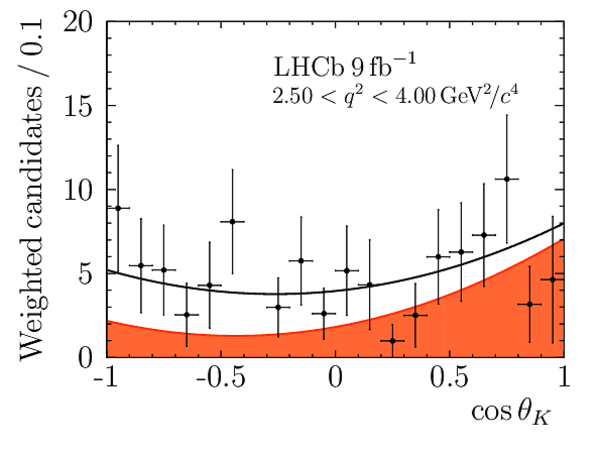
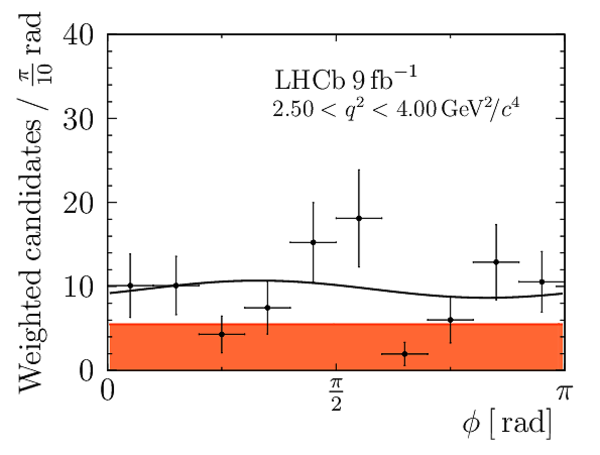
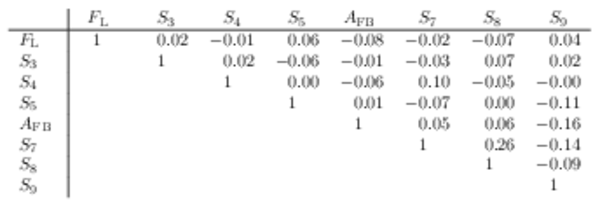
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $2.5< q^2 <4.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_5.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
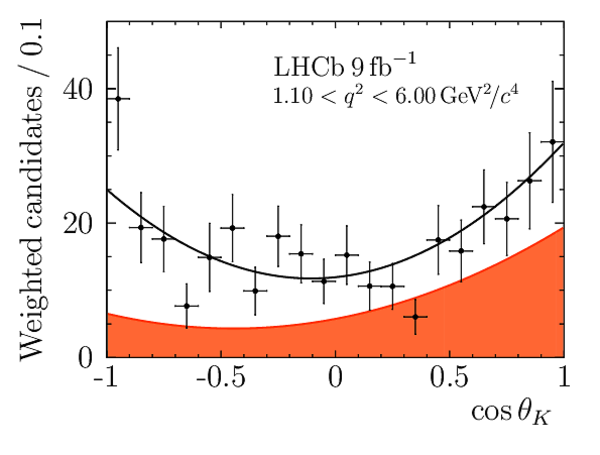
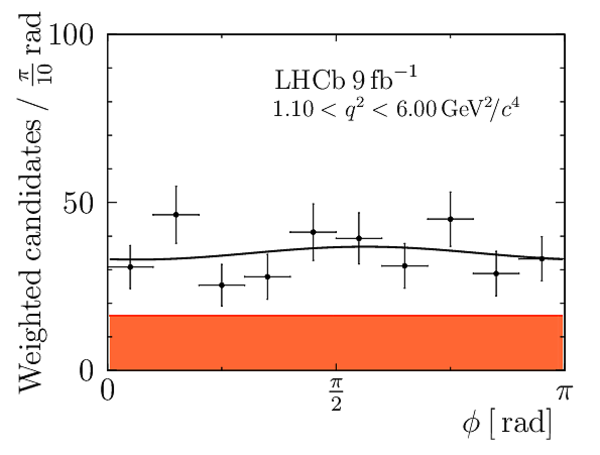
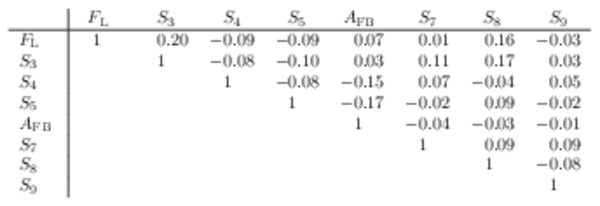
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $4.0< q^2 <6.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_6.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
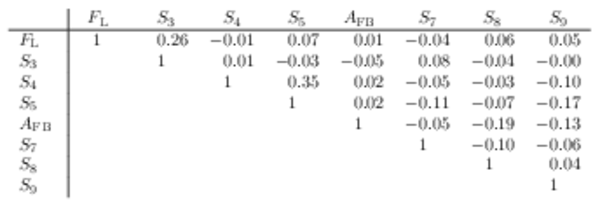
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $6.0< q^2 <8.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_7.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
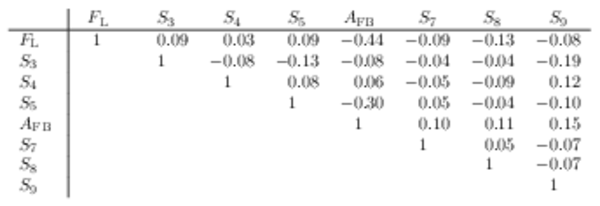
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $11.0< q^2 <12.5\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_8.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
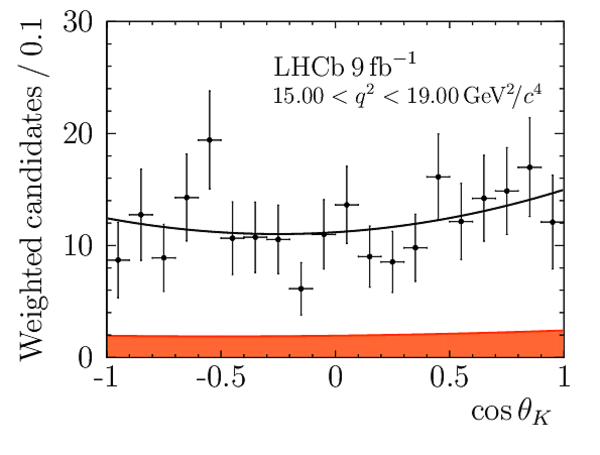
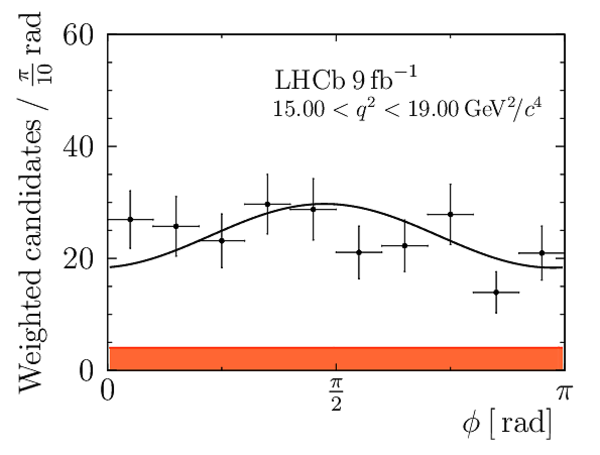
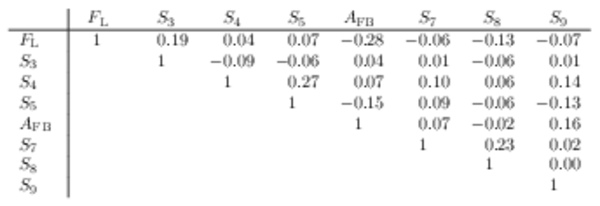
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $15.0< q^2 <17.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_9.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
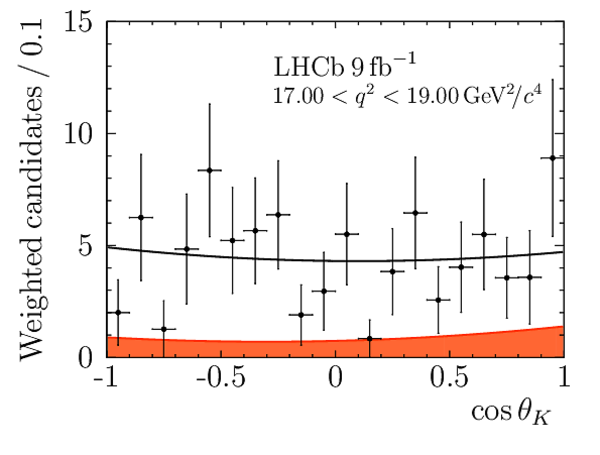
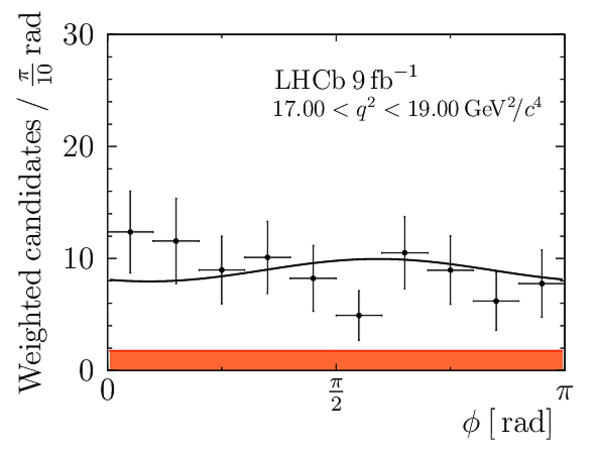
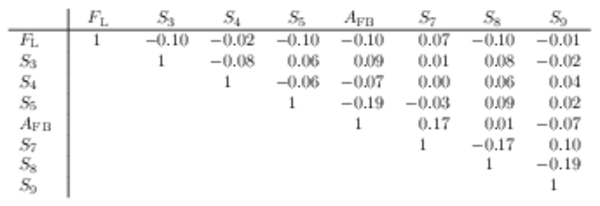
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $17.0< q^2 <19.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_10.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [44 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
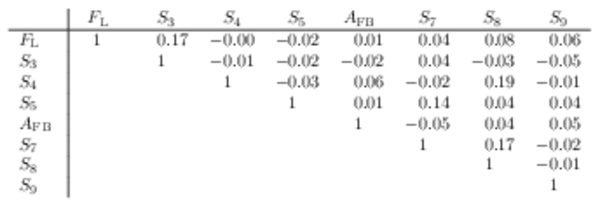
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $1.1< q^2 <6.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_11.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ , $ A_{\rm FB}$ and $S_{3} \text{--} S_{9}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $15.0< q^2 <19.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_12.pdf [50 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
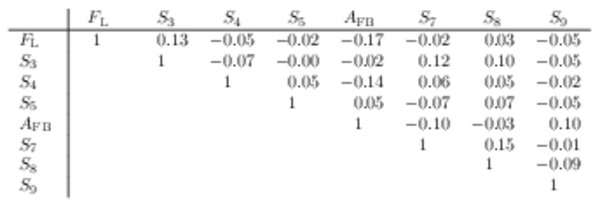
|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $0.10< q^2 <0.98\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_13.pdf [57 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $1.1< q^2 <2.5\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_14.pdf [57 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $2.5< q^2 <4.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_15.pdf [56 KiB] HiDef png [46 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $4.0< q^2 <6.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_16.pdf [57 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $6.0< q^2 <8.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_17.pdf [56 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $11.0< q^2 <12.5\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_18.pdf [56 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |
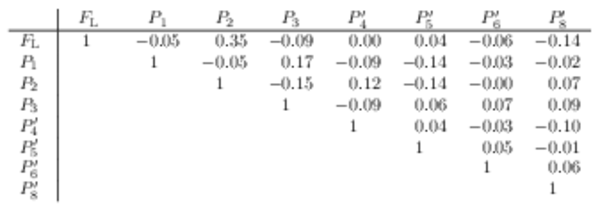
|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $15.0< q^2 <17.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_19.pdf [56 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |
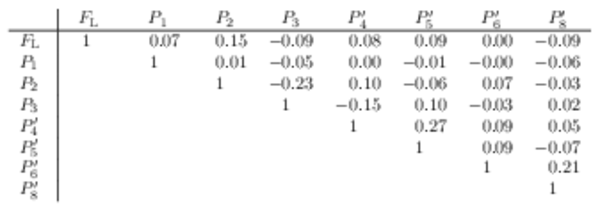
|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $17.0< q^2 <19.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_20.pdf [57 KiB] HiDef png [46 KiB] Thumbnail [22 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $1.1< q^2 <6.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_21.pdf [57 KiB] HiDef png [43 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |
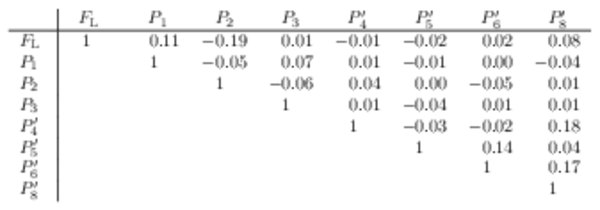
|
|
Correlation matrix for the $ C P$ -averaged observables $ F_{\rm L}$ and $P_{i}^{(\prime)}$ from the maximum-likelihood fit in the interval $15.0< q^2 <19.0\text{ Ge V} ^2 /c^4 $. |
Table_22.pdf [57 KiB] HiDef png [45 KiB] Thumbnail [21 KiB] tex code |

|
|
Maximum values for each source of systematic uncertainty. |
Table_23.pdf [61 KiB] HiDef png [94 KiB] Thumbnail [39 KiB] tex code |
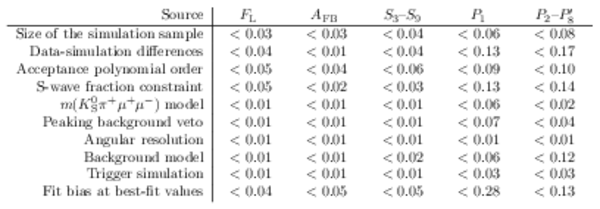
|
|
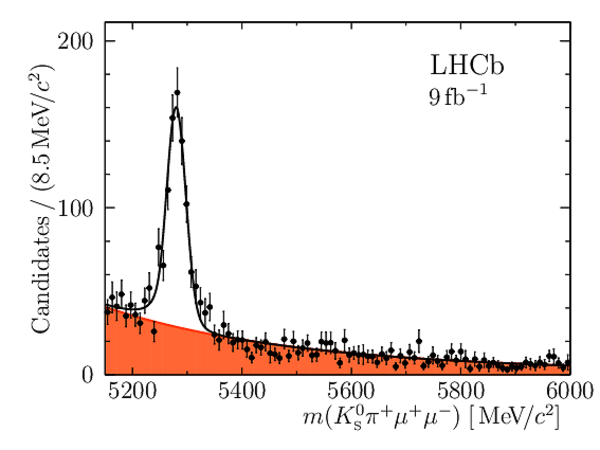
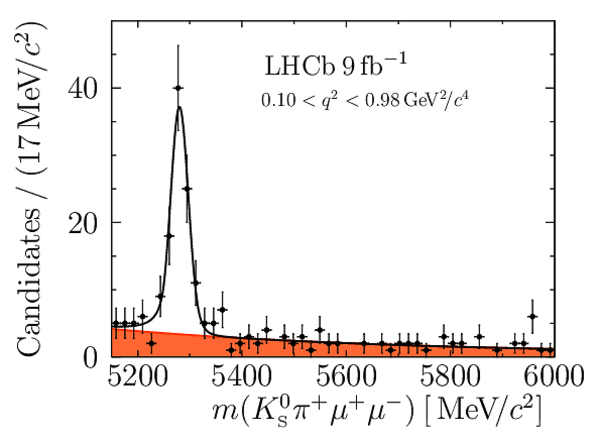
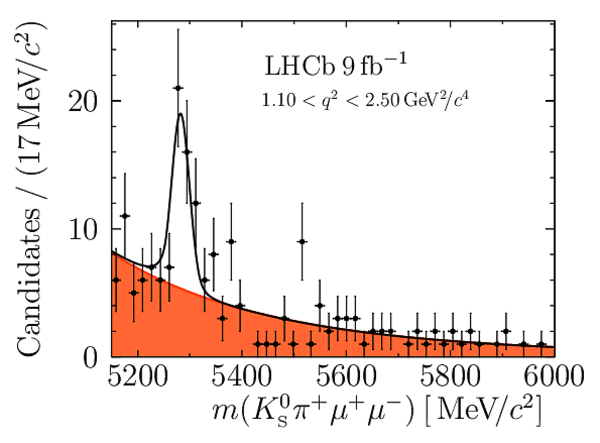
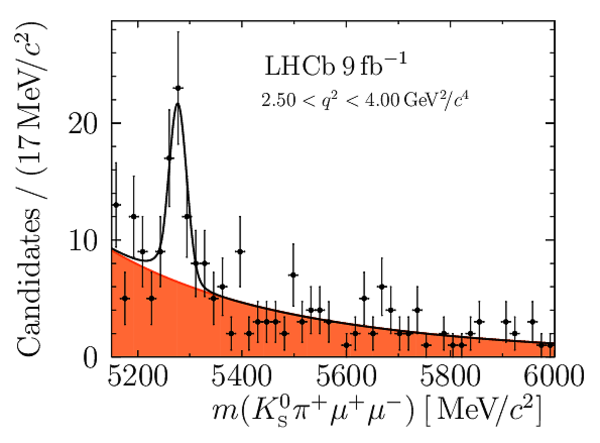
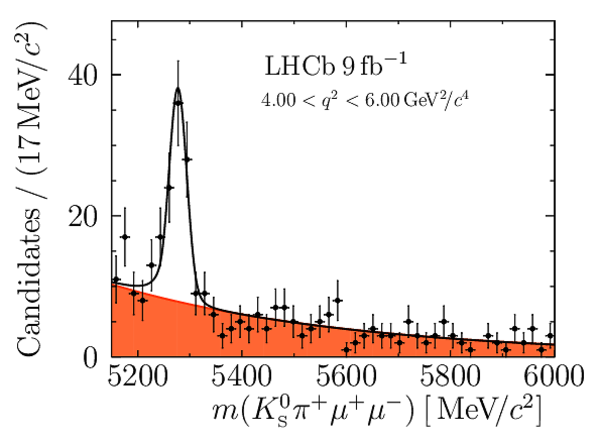
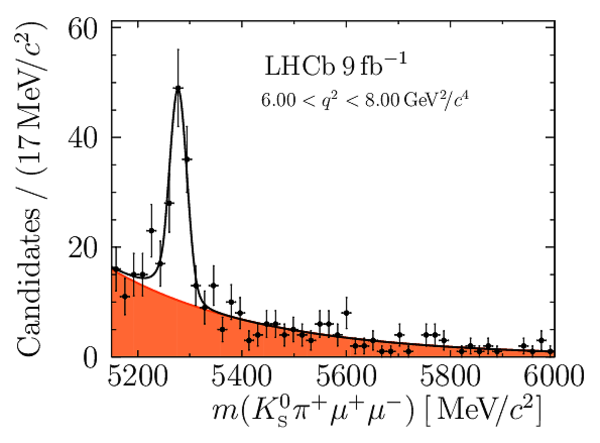
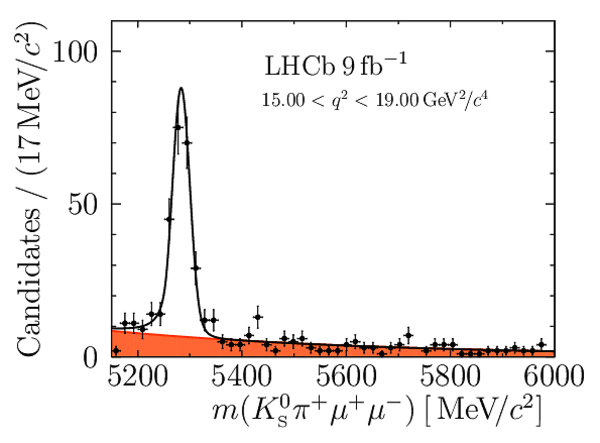
Yields of signal candidates in the ten $ q^2$ intervals. They are obtained from extended maximum-likelihood fits to the $m( K ^0_{\mathrm{S}} \pi ^+ \mu ^+\mu ^- )$ distribution. The total number corresponds to the sum of the eight nominal $ q^2$ intervals. |
Table_24.pdf [53 KiB] HiDef png [163 KiB] Thumbnail [78 KiB] tex code |
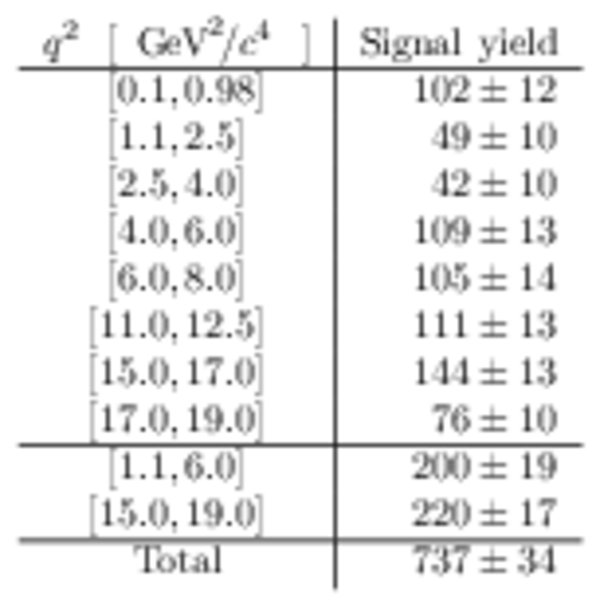
|
Supplementary Material [file]
| Supplementary material full pdf |
Supple[..].pdf [208 KiB] |
|
|
This ZIP file contains supplementary material for the publication LHCb-PAPER-2020-041. The files are: Supplementary.pdf : An overview of the extra figures Supplementary.tex : the LaTeX code of the supplementary material Fig9.pdf, Fig9.png, Fig9.eps : Figure 9 in various graphic formats Fig9.py, Fig9.csv : Figure 9 as python macro plus data values |
Fig9.pdf [146 KiB] HiDef png [160 KiB] Thumbnail [107 KiB] *C file |
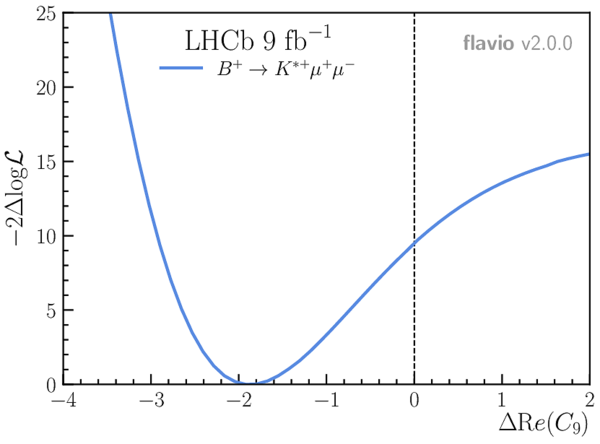
|
Created on 20 April 2024.