
Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-HIN-16-019 | ||
| Measurement of the skewness of elliptic flow fluctuations in PbPb collisions at $\sqrt{s_{\mathrm{NN}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| February 2017 | ||
| Abstract: Event-by-event flow harmonics are studied for PbPb collisions at $\sqrt{s_{\mathrm{NN}}} = $ 5.02 TeV using the CMS detector at the LHC. Flow harmonic probability distributions $p(v_2)$ are obtained using particles of 0.3 $ \leq p_{\mathrm{T}} \leq $ 3.0 GeV/$c$ and $|\eta| \leq $ 1.0 and are unfolded to remove smearing effects from observed azimuthal particle distributions. Cumulant flow harmonics are determined from the moments of $p(v_2)$ and used to estimate the standardized elliptic flow skewness in 5% wide centrality bins up to 60%. Hydrodynamic models predict that flow fluctuations will lead to a non-Gaussian component in the flow distributions with a negative skew with respect to the reaction plane. A significant negative skewness is observed for all centrality bins as evidenced by a splitting between $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ cumulants. In addition, elliptic power law distribution fits are made to the $p(v_2)$ distributions to infer information on the nature of initial-state eccentricity distributions. The elliptic power law parametrization is found to provide a more accurate description of the fluctuations than the Bessel-Gaussian parametrization. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
inSPIRE record ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, PLB 789 (2019) 643. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
Figure 1:
Fit performance of a Gaussian and Student's t-distribution to the rescaled subevent difference distributions for events in the 5-10% (top row) and 55-60% centrality classes (bottom row). Central events have a large number of tracks in each subevent, thus the Gaussian and Student's t-functions both describe the data well. The difference in fit performance is more pronounced in peripheral events where the small number of tracks per event is in the regime where the Student's t-function is relevant. |

png pdf |
Figure 2:
Cumulant values extracted from the unfolded $p ( v_2 )$ distributions exhibiting the expected $v_2\{2\} > v_2\{4\} \approx v_2\{6\} \approx v_2\{8\}$ behavior. Both statistical and systematic uncertainties are shown. A fine-level splitting of the higher-order cumulants becomes more pronounced in peripheral bins. |
png pdf |
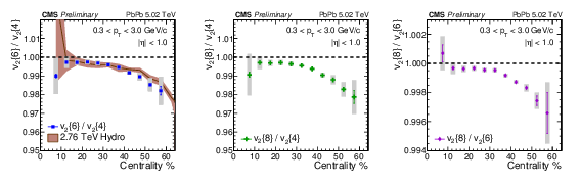
Figure 3:
Ratios of higher-order cumulants with values obtained from the moments of the unfolded $p ( v_2 )$ distributions. Both statistical and systematic uncertainties are shown. Hydrodynamic predictions for 2.76 TeV from Ref. [28] are presented as a colored band and are compared to the measured ratio $v_{2}\{6\}/v_2\{4\}$. Theory predictions are consistent to the measurement within uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 4:
The estimated skewness for the unfolded $p ( v_2 )$ as determined from its cumulant flow harmonics with Eq. 10. Both statistical and systematic uncertainties are shown. Hydrodynamic predictions for 2.76 TeV from Ref. [28] are presented as a colored band and are compared to the measured skewness. Theory predictions are consistent to the measurement within uncertainties. |
png pdf |
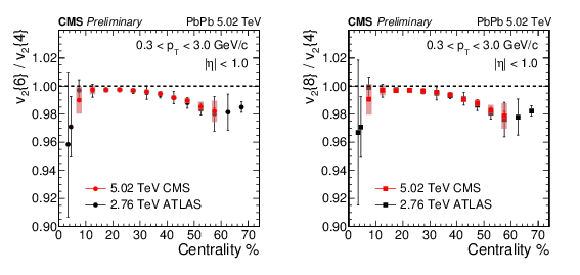
Figure 5:
Ratios of higher-order cumulants with values obtained from the moments of the unfolded $p ( v_2 )$ distributions measured by CMS compared to those measured by ATLAS in Ref. [27]. Both statistical and systematic uncertainties are shown for CMS as error bars and bands respectively. ATLAS uncertainties are presented as statistical and systematic added in quadrature. |

png pdf |
Figure 6:
Elliptic power law (Eq. 19) and Bessel-Gaussian (Eq. 5) parametrizations fitted to unfolded $p(v_2)$ distributions. Parameters extracted from each fit are provided in each panel with respective statistical uncertainties. All parameters except $\alpha $ are reported as percentages. Fit performance, as measured by the smeared-space $\chi ^2/$NDF goodness-of-fit, is presented as a function of centrality for each parametrization. |
| Summary |
| In summary, non-Gaussian behavior in the fluctuations of $v_2$ coefficients has been observed in PbPb collisions at $\sqrt{s_{\mathrm{NN}}} = $ 5.02 TeV. This observation was made by unfolding the statistical smearing effects in observed flow harmonic distributions to obtain the underlying event-by-event flow distributions for 5% wide centrality bins up to 60%. Cumulant flow harmonics were calculated from the moments of the underlying distributions and a fine-structure splitting was observed between $v_2\{4\}$, $v_2\{6\}$, and $v_2\{8\}$. In addition, the standardized skewness with respect to the reaction plane was estimated using the cumulants and was found to have a non-zero value, whose magnitude increases with centrality. Both measurements are consistent with a breakdown in the Gaussian model of elliptic flow fluctuations. In addition, Bessel-Gaussian and elliptic power law parametrizations were fitted to the unfolded $p(v_2)$ distributions to gain further insight as to the nature of the initial-state fluctuations. Both parametrizations assume a linear response between eccentricity and flow, but only the elliptic power law contains the physical constraint $\varepsilon_{2} < $ 1. This constraint naturally incorporates skewness and allows the elliptic power law parametrization to provide a more accurate description of $p(v_2)$ (and ultimately $p(\varepsilon_2)$) than the Bessel-Gaussian parametrization. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | BRAHMS Collaboration | Quark gluon plasma and color glass condensate at RHIC? The Perspective from the BRAHMS experiment | Nucl. Phys. A757 (2005) 1--27 | nucl-ex/0410020 |
| 2 | PHENIX Collaboration | Formation of dense partonic matter in relativistic nucleus-nucleus collisions at RHIC: Experimental evaluation by the PHENIX collaboration | Nucl. Phys. A757 (2005) 184--283 | nucl-ex/0410003 |
| 3 | B. B. Back et al. | The PHOBOS perspective on discoveries at RHIC | Nucl. Phys. A757 (2005) 28--101 | nucl-ex/0410022 |
| 4 | STAR Collaboration | Experimental and theoretical challenges in the search for the quark gluon plasma: The STAR Collaboration's critical assessment of the evidence from RHIC collisions | Nucl. Phys. A757 (2005) 102--183 | nucl-ex/0501009 |
| 5 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a Centrality-Dependent Dijet Asymmetry in Lead-Lead Collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{NN}}= $ 2.77 TeV with the ATLAS Detector at the LHC | PRL 105 (2010) 252303 | 1011.6182 |
| 6 | CMS Collaboration | Observation and studies of jet quenching in PbPb collisions at nucleon-nucleon center-of-mass energy of 2.76 TeV | PRC84 (2011) 024906 | CMS-HIN-10-004 1102.1957 |
| 7 | H. Song | QGP viscosity at RHIC and the LHC - a 2012 status report | Nucl. Phys. A904-905 (2013) 114c--121c | 1210.5778 |
| 8 | U. Heinz, C. Shen, and H. Song | The viscosity of quark-gluon plasma at RHIC and the LHC | AIP Conf. Proc. 1441 (2012) 766--770 | 1108.5323 |
| 9 | J.-Y. Ollitrault | Anisotropy as a signature of transverse collective flow | PRD46 (1992) 229--245 | |
| 10 | B. Alver and G. Roland | Collision geometry fluctuations and triangular flow in heavy-ion collisions | PRC81 (2010) 054905, , [Erratum: Phys. Rev.C82,039903(2010)] | 1003.0194 |
| 11 | M. L. Miller, K. Reygers, S. J. Sanders, and P. Steinberg | Glauber modeling in high energy nuclear collisions | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 57 (2007) 205--243 | nucl-ex/0701025 |
| 12 | D. Teaney and L. Yan | Triangularity and Dipole Asymmetry in Heavy Ion Collisions | PRC83 (2011) 064904 | 1010.1876 |
| 13 | S. A. Voloshin, A. M. Poskanzer, A. Tang, and G. Wang | Elliptic flow in the Gaussian model of eccentricity fluctuations | PLB659 (2008) 537--541 | 0708.0800 |
| 14 | L. Yan and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Universal fluctuation-driven eccentricities in proton-proton, proton-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus collisions | PRL 112 (2014) 082301 | 1312.6555 |
| 15 | Z. Qiu and U. W. Heinz | Event-by-event shape and flow fluctuations of relativistic heavy-ion collision fireballs | PRC84 (2011) 024911 | 1104.0650 |
| 16 | S. A. Voloshin, A. M. Poskanzer, and R. Snellings | Collective phenomena in non-central nuclear collisions | 0809.2949 | |
| 17 | D. A. Teaney | Viscous Hydrodynamics and the Quark Gluon Plasma | 0905.2433 | |
| 18 | S. Voloshin and Y. Zhang | Flow study in relativistic nuclear collisions by Fourier expansion of Azimuthal particle distributions | Z. Phys. C70 (1996) 665--672 | hep-ph/9407282 |
| 19 | N. Borghini, P. M. Dinh, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | A New method for measuring azimuthal distributions in nucleus-nucleus collisions | PRC63 (2001) 054906 | nucl-th/0007063 |
| 20 | N. Borghini, P. M. Dinh, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Flow analysis from multiparticle azimuthal correlations | PRC64 (2001) 054901 | nucl-th/0105040 |
| 21 | N. Borghini, P. M. Dinh, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Flow analysis from cumulants: A Practical guide | in International Workshop on the Physics of the Quark Gluon Plasma Palaiseau, France, 2001 | nucl-ex/0110016 |
| 22 | J. Jia | Event-shape fluctuations and flow correlations in ultra-relativistic heavy-ion collisions | JPG41 (2014), no. 12, 124003 | 1407.6057 |
| 23 | R. S. Bhalerao, M. Luzum, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Determining initial-state fluctuations from flow measurements in heavy-ion collisions | PRC84 (2011) 034910 | 1104.4740 |
| 24 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the distributions of event-by-event flow harmonics in lead-lead collisions at 2.76 TeV with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | JHEP 11 (2013) 183 | 1305.2942 |
| 25 | CMS Collaboration Collaboration | Azimuthal anisotropy of charged particles from multiparticle correlations in pPb and PbPb collisions with CMS | CMS-CR-2014-160 | |
| 26 | ALICE Collaboration | Multiparticle azimuthal correlations in p -Pb and Pb-Pb collisions at the CERN Large Hadron Collider | PRC90 (2014), no. 5, 054901 | 1406.2474 |
| 27 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of flow harmonics with multi-particle cumulants in Pb+Pb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{\mathrm {NN}}}= $ 2.76 TeV with the ATLAS detector | EPJC74 (2014), no. 11 | 1408.4342 |
| 28 | G. Giacalone, L. Yan, J. Noronha-Hostler, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | The skewness of elliptic flow fluctuations | 1608.01823 | |
| 29 | H. Gronqvist, J.-P. Blaizot, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Non-Gaussian eccentricity fluctuations | 1604.07230 | |
| 30 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 31 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 32 | T. Sj\"ostrand, S. Mrenna, and P. Skands | PYTHIA 6.4 physics and manual | JHEP 05 (2006) 026 | hep-ph/0603175 |
| 33 | I. P. Lokhtin and A. M. Snigirev | A Model of jet quenching in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions and high-p(T) hadron spectra at RHIC | EPJC45 (2006) 211--217 | hep-ph/0506189 |
| 34 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4: A Simulation toolkit | NIMA506 (2003) 250--303 | |
| 35 | A. M. Poskanzer and S. A. Voloshin | Methods for analyzing anisotropic flow in relativistic nuclear collisions | PRC58 (1998) 1671--1678 | nucl-ex/9805001 |
| 36 | G. D'Agostini | A Multidimensional unfolding method based on Bayes' theorem | Nucl.Instrum.Meth. A362 (1995) 487--498 | |
| 37 | W. H. Richardson | Bayesian-based iterative method of image restoration | JOSA 62 (1972), no. 1, 55--59 | |
| 38 | L. B. Lucy | An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions | The astronomical journal 79 (1974) 745 | |
| 39 | J. Jia and S. Mohapatra | Disentangling flow and nonflow correlations via Bayesian unfolding of the event-by-event distributions of harmonic coefficients in ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions | PRC88 (2013), no. 1, 014907 | 1304.1471 |
| 40 | T. Adye | Unfolding algorithms and tests using RooUnfold | in Proceedings of the PHYSTAT 2011 Workshop, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland, January 2011, CERN-2011-006, pp 313-318, pp. 313--318 2011 | 1105.1160 |
| 41 | R. Brun and F. Rademakers | ROOT: An object oriented data analysis framework | NIMA389 (1997) 81--86 | |
| 42 | B. H. Alver, C. Gombeaud, M. Luzum, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Triangular flow in hydrodynamics and transport theory | PRC82 (2010) 034913 | 1007.5469 |
| 43 | B. Schenke, S. Jeon, and C. Gale | Elliptic and Triangular Flow in Event-by-Event D=3+1 Viscous Hydrodynamics | PRL 106 (2011) 042301 | |
| 44 | Z. Qiu, C. Shen, and U. W. Heinz | Hydrodynamic elliptic and triangular flow in Pb-Pb collisions at $ \sqrt{s_{_{\mathrm{NN}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | PLB 707 (2012) 151 | 1110.3033 |
| 45 | L. Yan, J.-Y. Ollitrault, and A. M. Poskanzer | Universal parameterization of initial-state fluctuations and its applications to event-by-event anisotropy | Nucl. Phys. A931 (2014) 1007--1011 | 1408.0709 |
| 46 | L. Yan, J.-Y. Ollitrault, and A. M. Poskanzer | Azimuthal Anisotropy Distributions in High-Energy Collisions | PLB 742 (2015) 290 | 1408.0921 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|
|
|
|
|

|