




Next: Multipoles
Up: The MAD Program
Previous: Basic Language Format
Following the CLASSIC standard, the phase-space coordinates are now:
where  is the constant momentum of a "synchronous"
particle, and
is the constant momentum of a "synchronous"
particle, and 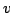 is the instantaneous velocity of the particle.
is the instantaneous velocity of the particle.
chris.iselin@cern.ch