Large-R (anti-kt R=1.0) JES and JMS for 2012 data
Jet Energy Scale
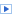
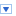
| Summary of the trimmed jet pT scale (JpTS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of jet pT. Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from [1] Track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT; [2] Gamma+jet response in data and [3] Pileup dependence are calculated using the full 2012 dataset with the same prescription as for regular jets with no jet area or offset pileup corrections (as in arXiv:1406.0076); [4] Monte Carlo -based studies of response differences across the different final state topologies resulting from QCD dijet, ttbar and W+jet production. It is known that the pT scale of anti-kt, R = 0.4 jets differs depending on whether the jet was quark- or gluon- initiated [arxiv:1112.6426, arXiv:1406.0076]. By analogy, the jet pT scale may differ between jets originating from quark/gluon and those originating from a W boson or top quark. An internal MC study comparing the jet pT scale for top-, W- and quark/gluon-initiated jets provided by Powheg revealed differences in the pT scale of up to 2-4% dependent on the jet ’flavor’ (or topology) and pT. Repeated studies using the Pythia8, MC@NLO and MadGraph generators support these conclusions. |  [eps] |
| Summary of the trimmed jet pT scale (JpTS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of jet pT. Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from [1] Track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT; [2] Gamma+jet response in data and [3] Pileup dependence are calculated using the full 2012 dataset with the same prescription as for regular jets with no jet area or offset pileup corrections (as in arXiv:1406.0076); [4] Monte Carlo -based studies of response differences across the different final state topologies resulting from QCD dijet, ttbar and W+jet production. It is known that the pT scale of anti-kt, R = 0.4 jets differs depending on whether the jet was quark- or gluon- initiated [arxiv:1112.6426, arXiv:1406.0076]. By analogy, the jet pT scale may differ between jets originating from quark/gluon and those originating from a W boson or top quark. An internal MC study comparing the jet pT scale for top-, W- and quark/gluon-initiated jets provided by Powheg revealed differences in the pT scale of up to 2-4% dependent on the jet ’flavor’ (or topology) and pT. Repeated studies using the Pythia8, MC@NLO and MadGraph generators support these conclusions. |  [eps] |
| Summary of the trimmed jet pT scale (JpTS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of jet pT. Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from [1] Track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT; [2] Gamma+jet response in data and [3] Pileup dependence are calculated using the full 2012 dataset with the same prescription as for regular jets with no jet area or offset pileup corrections (as in arXiv:1406.0076); [4] Monte Carlo -based studies of response differences across the different final state topologies resulting from QCD dijet, ttbar and W+jet production. It is known that the pT scale of anti-kt, R = 0.4 jets differs depending on whether the jet was quark- or gluon- initiated [arxiv:1112.6426, arXiv:1406.0076]. By analogy, the jet pT scale may differ between jets originating from quark/gluon and those originating from a W boson or top quark. An internal MC study comparing the jet pT scale for top-, W- and quark/gluon-initiated jets provided by Powheg revealed differences in the pT scale of up to 2-4% dependent on the jet ’flavor’ (or topology) and pT. Repeated studies using the Pythia8, MC@NLO and MadGraph generators support these conclusions. |  [eps] |
| Summary of the trimmed jet pT scale (JpTS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of jet pT. Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from [1] Track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT; [2] Gamma+jet response in data and [3] Pileup dependence are calculated using the full 2012 dataset with the same prescription as for regular jets with no jet area or offset pileup corrections (as in arXiv:1406.0076); [4] Monte Carlo -based studies of response differences across the different final state topologies resulting from QCD dijet, ttbar and W+jet production. It is known that the pT scale of anti-kt, R = 0.4 jets differs depending on whether the jet was quark- or gluon- initiated [arxiv:1112.6426, arXiv:1406.0076]. By analogy, the jet pT scale may differ between jets originating from quark/gluon and those originating from a W boson or top quark. An internal MC study comparing the jet pT scale for top-, W- and quark/gluon-initiated jets provided by Powheg revealed differences in the pT scale of up to 2-4% dependent on the jet ’flavor’ (or topology) and pT. Repeated studies using the Pythia8, MC@NLO and MadGraph generators support these conclusions. | 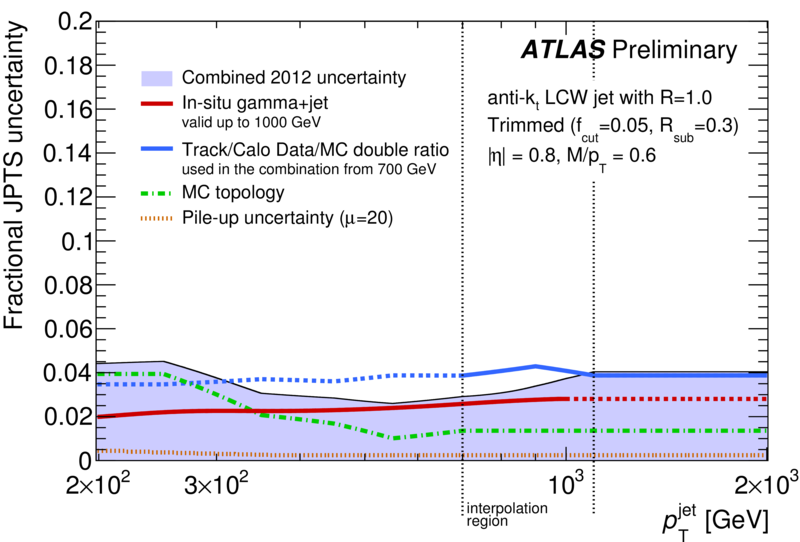 [eps] |
| Summary of the trimmed jet pT scale (JpTS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of jet pT. Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from [1] Track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT; [2] Gamma+jet response in data and [3] Pileup dependence are calculated using the full 2012 dataset with the same prescription as for regular jets with no jet area or offset pileup corrections (as in arXiv:1406.0076); [4] Monte Carlo -based studies of response differences across the different final state topologies resulting from QCD dijet, ttbar and W+jet production. It is known that the pT scale of anti-kt, R = 0.4 jets differs depending on whether the jet was quark- or gluon- initiated [arxiv:1112.6426, arXiv:1406.0076]. By analogy, the jet pT scale may differ between jets originating from quark/gluon and those originating from a W boson or top quark. An internal MC study comparing the jet pT scale for top-, W- and quark/gluon-initiated jets provided by Powheg revealed differences in the pT scale of up to 2-4% dependent on the jet ’flavor’ (or topology) and pT. Repeated studies using the Pythia8, MC@NLO and MadGraph generators support these conclusions. | 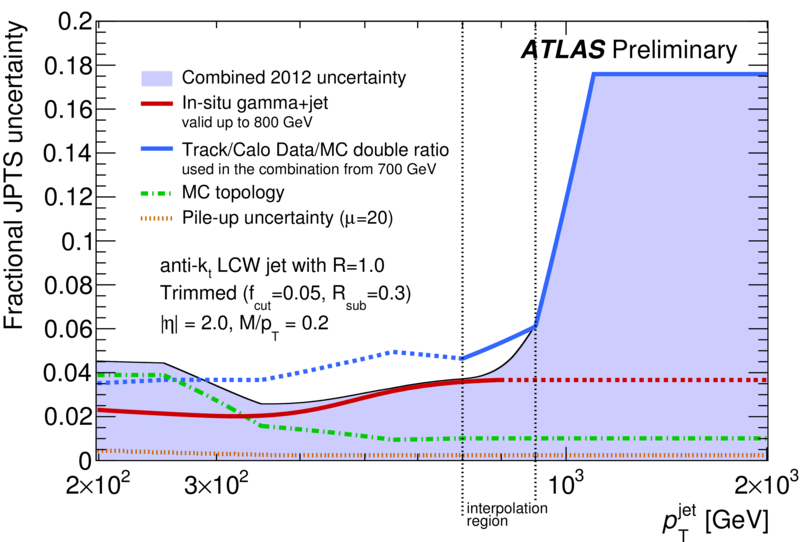 [eps] |
| Summary of the trimmed jet pT scale (JpTS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of jet pT. Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from [1] Track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT; [2] Gamma+jet response in data and [3] Pileup dependence are calculated using the full 2012 dataset with the same prescription as for regular jets with no jet area or offset pileup corrections (as in arXiv:1406.0076); [4] Monte Carlo -based studies of response differences across the different final state topologies resulting from QCD dijet, ttbar and W+jet production. It is known that the pT scale of anti-kt, R = 0.4 jets differs depending on whether the jet was quark- or gluon- initiated [arxiv:1112.6426, arXiv:1406.0076]. By analogy, the jet pT scale may differ between jets originating from quark/gluon and those originating from a W boson or top quark. An internal MC study comparing the jet pT scale for top-, W- and quark/gluon-initiated jets provided by Powheg revealed differences in the pT scale of up to 2-4% dependent on the jet ’flavor’ (or topology) and pT. Repeated studies using the Pythia8, MC@NLO and MadGraph generators support these conclusions. | 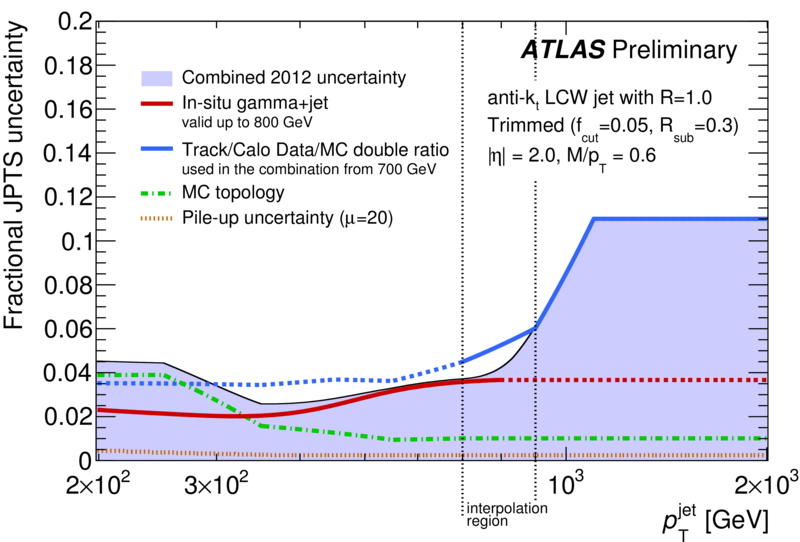 [eps] |
Jet Mass Scale
| Summary of the trimmed jet mass scale (JMS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of pjet . T Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT. | 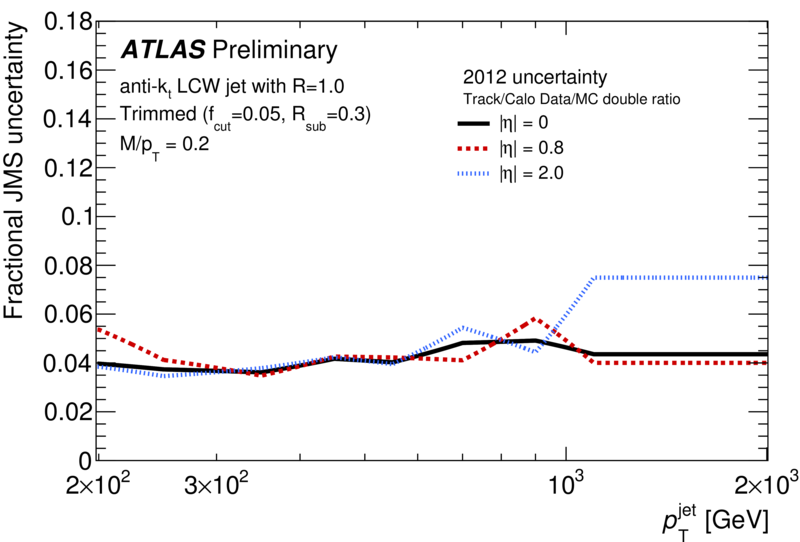 [eps] |
| Summary of the trimmed jet mass scale (JMS) fractional systematic uncertainties as a function of pjet . T Trimming is implemented (as in arXiv:1306.4945) by re-clustering the jet constituents into subjets of radius R=0.3. The clusters belonging to subjets that carry at least 5% of the original jet pT are kept, and those clusters in subjets with less than 5% of the original jet pT are discarded. These uncertainties are determined from track/calo jet double ratios using the same prescription as for 2011 (arXiv:1306.4945), which includes a contribution from the tracking efficiency and fake rate. In 2011 the uncertainties were determine as a function of pT and eta; this has been updated such that uncertainties are now calculated as a function of pT, eta and mass/pT. | 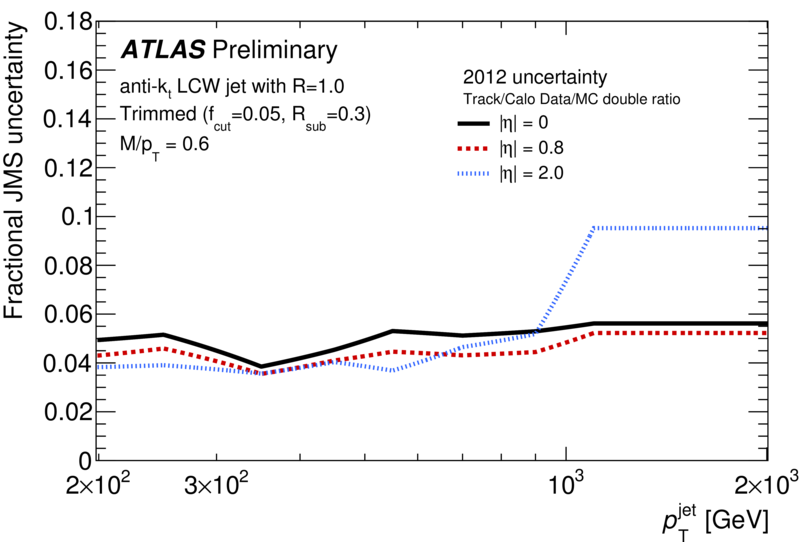 [eps] |
-- DavidLopezMateos - 17 Aug 2014 Responsible: DavidLopezMateos
Subject: public
| I | Attachment | History | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
JMS_mop020.eps | r1 | manage | 23.1 K | 2014-08-17 - 15:53 | DavidLopezMateos | |
| |
JMS_mop020.png | r1 | manage | 230.9 K | 2014-08-17 - 15:53 | DavidLopezMateos | |
| |
JMS_mop060.eps | r1 | manage | 23.1 K | 2014-08-17 - 15:52 | DavidLopezMateos | |
| |
JMS_mop060.png | r1 | manage | 237.4 K | 2014-08-17 - 15:52 | DavidLopezMateos |
Topic revision: r2 - 2014-08-18 - DavidLopezMateos
or Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? use Discourse or Send feedback