
Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-EXO-16-039 | ||
| Search for dark matter and graviton produced in association with a photon in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with an integrated luminosity of 12.9 fb$^{-1}$ | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| August 2016 | ||
| Abstract: A search is conducted for dark matter pair-production and for graviton production predicted by the ADD large extra dimensions model in a final state with a photon and missing transverse energy in pp collisions at $\sqrt{s}=$ 13 TeV. Data taken by the CMS experiment in 2016 corresponding to an integrated luminosity of 12.9 fb$^{-1}$ is analyzed. A Poisson counting technique is used to assess a potential excess of events with respect to background, estimated through simulation and data-driven methods. No such excess is observed. The results of the searches are interpreted as exclusion limits in the model parameter spaces. | ||
|
Links:
CDS record (PDF) ;
inSPIRE record ;
CADI line (restricted) ;
These preliminary results are superseded in this paper, JHEP 10 (2017) 073. The superseded preliminary plots can be found here. |
||
| Figures | |

png pdf |
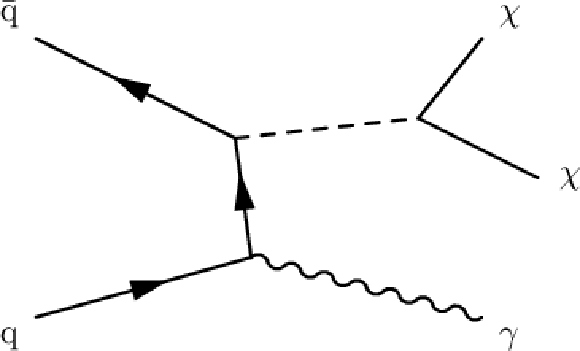
Figure 1:
Example diagrams of new-physics interactions that lead to a final state of $ {\gamma }$ and large missing transverse momentum. |
png pdf |
Figure 1-a:
Example diagram of new-physics interactions that lead to a final state of $ {\gamma }$ and large missing transverse momentum. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
Example diagram of new-physics interactions that lead to a final state of $ {\gamma }$ and large missing transverse momentum. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-c:
Example diagram of new-physics interactions that lead to a final state of $ {\gamma }$ and large missing transverse momentum. |
png pdf |
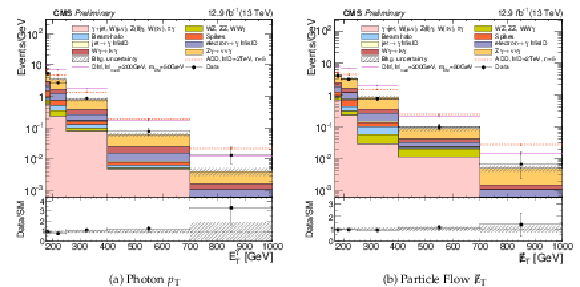
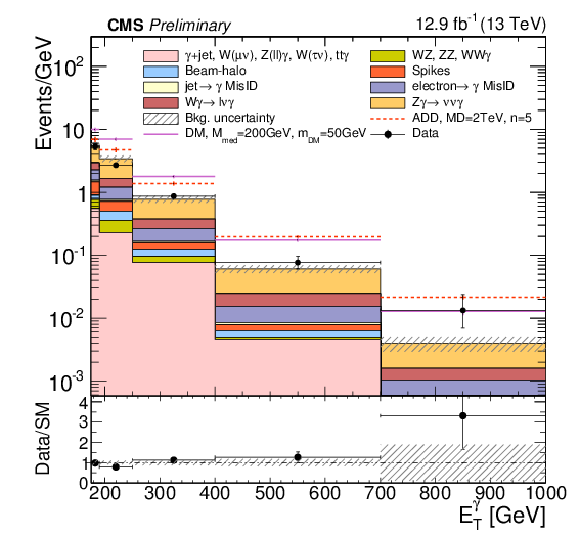
Figure 2:
The ${p_{\mathrm {T}}^{ {\gamma }}}$ and ${E_{\mathrm {T}}}^{\text{miss}} $ distributions for the candidate sample, compared with estimated contributions from SM backgrounds. Systematic and statistical uncertainties on the background estimates are added in quadrature. |
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
The ${p_{\mathrm {T}}^{ {\gamma }}}$ distribution for the candidate sample, compared with estimated contributions from SM backgrounds. Systematic and statistical uncertainties on the background estimates are added in quadrature. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
The ${E_{\mathrm {T}}}^{\text{miss}} $ distributions for the candidate sample, compared with estimated contributions from SM backgrounds. Systematic and statistical uncertainties on the background estimates are added in quadrature. |

png pdf |
Figure 3:
95% CL upper limits on $\mu = \sigma $/$\sigma _{\text {Theory}}$ in the ${M_{\text {med}}}- {m_{\text {DM}}}$ plane for vector and axial-vector mediator, assuming $g_{ {\mathrm {q}}}=$ 0.25 and $g_{\chi }=$ 1. Expected and observed exclusion contours are overlaid, where mass points to the lower left of the curves are excluded. |

png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
95% CL upper limits on $\mu = \sigma $/$\sigma _{\text {Theory}}$ in the ${M_{\text {med}}}- {m_{\text {DM}}}$ plane for a vector mediator, assuming $g_{ {\mathrm {q}}}=$ 0.25 and $g_{\chi }=$ 1. Expected and observed exclusion contours are overlaid, where mass points to the lower left of the curves are excluded. |
png pdf |
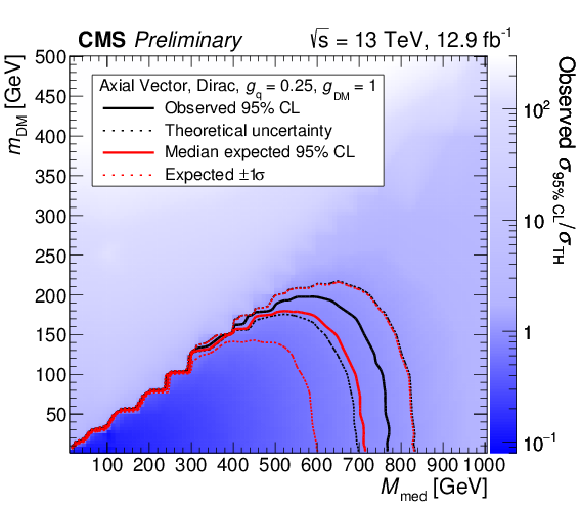
Figure 3-b:
95% CL upper limits on $\mu = \sigma $/$\sigma _{\text {Theory}}$ in the ${M_{\text {med}}}- {m_{\text {DM}}}$ plane for an axial-vector mediator, assuming $g_{ {\mathrm {q}}}=$ 0.25 and $g_{\chi }=$ 1. Expected and observed exclusion contours are overlaid, where mass points to the lower left of the curves are excluded. |
png pdf |
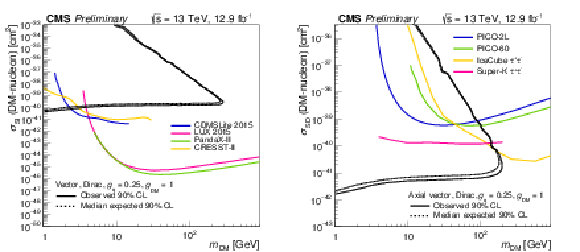
Figure 4:
The 90% CL exclusion limits on the $\chi $-nucleon scattering cross section in a simplified model of dark matter production involving a vector and axial-vector operator as a function of the ${m_{\text {DM}}}$. The region to the upper left of the contour is excluded. Shown together are corresponding exclusion contours, where regions above the curves are excluded, from the recent results by CDMSLite [27], LUX [28], PandaX [29], CRESST-II [30], PICO-2L [31], PICO-60 [32], IceCube [33], and SuperKamiokande [34] collaborations. |
png pdf |
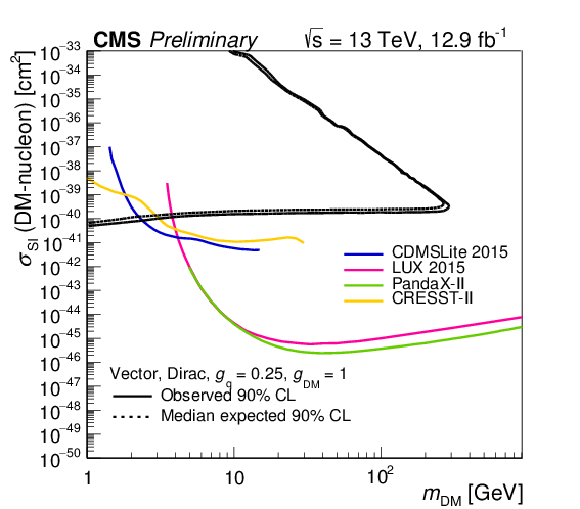
Figure 4-a:
The 90% CL exclusion limits on the $\chi $-nucleon scattering cross section in a simplified model of dark matter production involving a vector operator as a function of the ${m_{\text {DM}}}$. The region to the upper left of the contour is excluded. Shown together are corresponding exclusion contours, where regions above the curves are excluded, from the recent results by CDMSLite [27], LUX [28], PandaX [29], CRESST-II [30], PICO-2L [31], PICO-60 [32], IceCube [33], and SuperKamiokande [34] collaborations. |
png pdf |
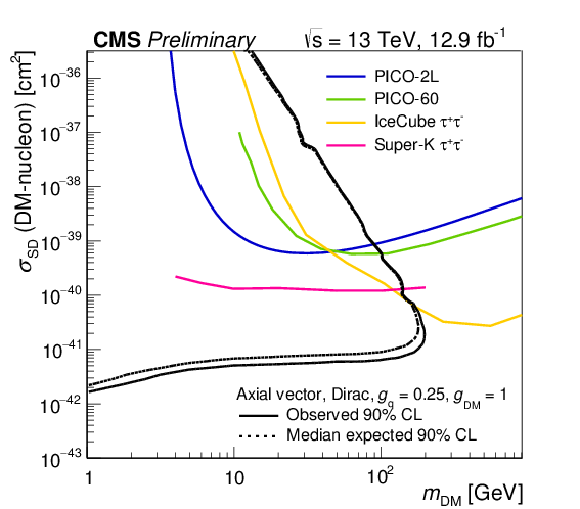
Figure 4-b:
The 90% CL exclusion limits on the $\chi $-nucleon scattering cross section in a simplified model of dark matter production involving an axial-vector operator as a function of the ${m_{\text {DM}}}$. The region to the upper left of the contour is excluded. Shown together are corresponding exclusion contours, where regions above the curves are excluded, from the recent results by CDMSLite [27], LUX [28], PandaX [29], CRESST-II [30], PICO-2L [31], PICO-60 [32], IceCube [33], and SuperKamiokande [34] collaborations. |
png pdf |
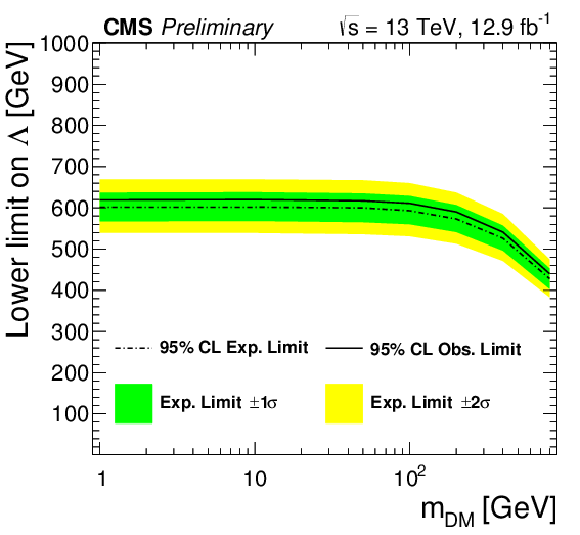
Figure 5:
The 95% CL expected and observed lower limits on $\Lambda $ for a dimension-7 operator EFT model with a contact interaction of type $\gamma \gamma \chi \overline {\chi }$ as a function of dark matter mass ${m_{\text {DM}}}$. |

png pdf |
Figure 6:
The 95% CL upper limits on the ADD graviton production cross sections as a function of ${M_D}$ for $n=3$. |
png pdf |
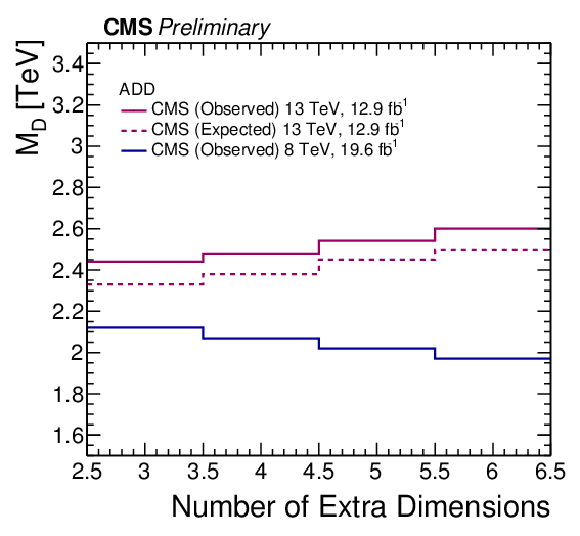
Figure 7:
Lower limit on ${M_D}$ as a function of $n$. |
| Tables | |
png pdf |
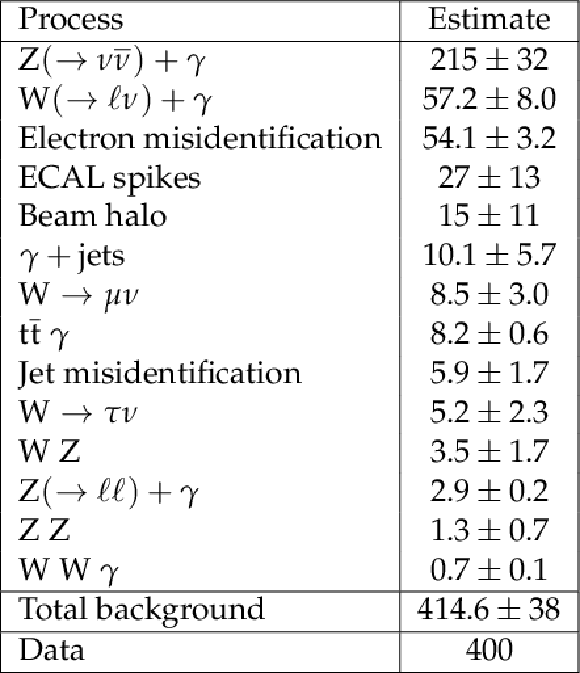
Table 1:
Summary of estimated backgrounds and observed total number of candidates. Systematic and statistical uncertainties on the background estimates are added in quadrature. |
png pdf |
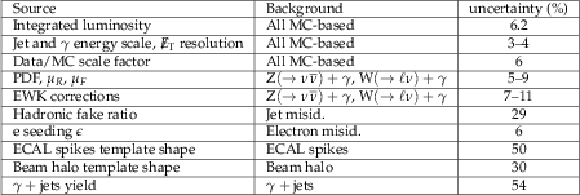
Table 2:
Summary of relative systematic uncertainties (%) for different background estimates. |
png pdf |
Table 3:
95% CL observed and expected lower limits on ${M_D}$ as a function of $n$. |
| Summary |
| Proton-proton collision events containing a photon and missing transverse momentum have been investigated to search for new phenomena. In the $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV data set corresponding to 12.9 fb$^{-1}$ of integrated luminosity, no deviations from the standard model predictions are observed. Upper limits are obtained on dark matter and ADD graviton production cross sections at 95% confidence level, which are then translated to limits on relevant parameters of the individual models. For the simplified dark matter production models considered, the search excludes mediator masses of up to 760 GeV for massless dark matter. For an effective dimension-7 photon-dark matter contact interaction, values of the suppression scale up to 620 GeV are excluded. For ADD extra dimensions, gravitational energy scale up to 2.44-2.60 TeV, depending on the number of extra dimensions, are excluded. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | R. Gaitskell | Direct Detection of Dark Matter | Annual Review of Nuclear and Particle Science 54 (2004) | |
| 2 | N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos, and G. Dvali | The Hierarchy problem and new dimensions at a millimeter | PLB 429 (1998) 263 | hep-ph/9803315 |
| 3 | A. Nelson et al. | Confronting the Fermi Line with LHC data: an Effective Theory of Dark Matter Interaction with Photons | PRD89 (2014), no. 5, 056011 | 1307.5064 |
| 4 | D. Abercrombie et al. | Dark Matter Benchmark Models for Early LHC Run-2 Searches: Report of the ATLAS/CMS Dark Matter Forum | 1507.00966 | |
| 5 | CMS Collaboration | Search for Dark Matter and Large Extra Dimensions in the gamma + MET final state in pp Collisions at sqrt(s) = 13 TeV | ||
| 6 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in events with a photon and missing transverse momentum in $ pp $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s}=13 $ TeV with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 06 (2016) 059 | 1604.01306 |
| 7 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of Photon Reconstruction and Identification with the CMS Detector in Proton-Proton Collisions at sqrt(s) = 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015) P08010 | CMS-EGM-14-001 1502.02702 |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-Flow Event Reconstruction in CMS and Performance for Jets, Taus, and MET | CDS | |
| 10 | CMS Collaboration | Commissioning of the Particle-Flow Reconstruction in Minimum-Bias and Jet Events from pp Collisions at 7 TeV | CDS | |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of Photon Reconstruction and Identification with the CMS Detector in Proton-Proton Collisions at sqrt(s) = 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015), no. 08, P08010 | CMS-EGM-14-001 1502.02702 |
| 12 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-k$ _{\text{t}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 13 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS missing transverse momentum reconstruction in pp data at $ \sqrt{s} $ = 8 TeV | JINST 10 (2015), no. 02, P02006 | CMS-JME-13-003 1411.0511 |
| 14 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 15 | T. Sj\"ostrand et al. | An Introduction to PYTHIA 8.2 | CPC 191 (2015) 159--177 | 1410.3012 |
| 16 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4--a simulation toolkit | Nucl. Instrum. Meth A 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 17 | J. Allison et al. | Geant4 Developments and Applications | IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci 53 (2006) 270 | |
| 18 | S. Catani, D. de Florian, G. Ferrera, and M. Grazzini | Vector boson production at hadron colliders: transverse-momentum resummation and leptonic decay | JHEP 12 (2015) 047 | 1507.06937 |
| 19 | A. Denner, S. Dittmaier, M. Hecht, and C. Pasold | NLO QCD and electroweak corrections to W+$ \gamma $ production with leptonic W-boson decays | JHEP 04 (2015) 018 | 1412.7421 |
| 20 | A. Denner, S. Dittmaier, M. Hecht, and C. Pasold | NLO QCD and electroweak corrections to Z$ +\gamma $ production with leptonic Z-boson decays | JHEP 02 (2016) 057 | 1510.08742 |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | Isolated Photon Reconstruction and Identification at $ \sqrt{s}=7 $~TeV | CDS | |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | Measurements of Inclusive $ W $ and $ Z $ Cross Sections in $ pp $ Collisions at $ \sqrt{s}=7 $ TeV | JHEP 01 (2011) 080 | CMS-EWK-10-002 1012.2466 |
| 23 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIMA434 (1999) 435--443 | hep-ex/9902006 |
| 24 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: The CL(s) technique | JPG28 (2002) 2693--2704, .[,11(2002)] | |
| 25 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations, The LHC Higgs Combination Group | Procedure for the LHC Higgs boson search combination in Summer 2011 | CMS-NOTE-2011-005 | |
| 26 | G. Busoni et al. | Recommendations on presenting LHC searches for missing transverse energy signals using simplified $ s $-channel models of dark matter | 1603.04156 | |
| 27 | SuperCDMS Collaboration | New Results from the Search for Low-Mass Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with the CDMS Low Ionization Threshold Experiment | PRL 116 (2016), no. 7, 071301 | 1509.02448 |
| 28 | LUX Collaboration | Improved Limits on Scattering of Weakly Interacting Massive Particles from Reanalysis of 2013 LUX Data | PRL 116 (2016), no. 16, 161301 | 1512.03506 |
| 29 | PandaX-II Collaboration | Dark Matter Results from First 98.7-day Data of PandaX-II Experiment | 1607.07400 | |
| 30 | CRESST Collaboration | Results on light dark matter particles with a low-threshold CRESST-II detector | EPJC76 (2016), no. 1, 25 | 1509.01515 |
| 31 | PICO Collaboration | Improved dark matter search results from PICO-2L Run 2 | PRD93 (2016), no. 6, 061101 | 1601.03729 |
| 32 | PICO Collaboration | Dark matter search results from the PICO-60 CF$ _3 $I bubble chamber | PRD93 (2016), no. 5, 052014 | 1510.07754 |
| 33 | IceCube Collaboration | Improved limits on dark matter annihilation in the Sun with the 79-string IceCube detector and implications for supersymmetry | JCAP 1604 (2016), no. 04, 022 | 1601.00653 |
| 34 | Super-Kamiokande Collaboration | Search for neutrinos from annihilation of captured low-mass dark matter particles in the Sun by Super-Kamiokande | PRL 114 (2015), no. 14, 141301 | 1503.04858 |
| 35 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new phenomena in monophoton final states in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt s = $ 8 TeV | PLB755 (2016) 102--124 | CMS-EXO-12-047 1410.8812 |
| 36 | G. F. Giudice, R. Rattazzi, and J. D. Wells | Quantum gravity and extra dimensions at high-energy colliders | Nucl. Phys. B544 (1999) 3--38 | hep-ph/9811291 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|
|
|
|
|

|