
|
| Examples |
| Modules |
| Namespaces |
| Hierarchy |
| Classes Annotated Members |
| Globals |
| Files |
| Related Pages |
| Copyright |
| GSL-- homepage |
Matrices
[Vectors and maticies]
Collaboration diagram for Matrices:

|
Detailed Description
This group contains matrix classes, and classes and functions to manipulate matrices.The class matrix is the GSL-- representation of a matrix. It is implemented (as it is in GSL) as a dense matrix. That is, room for all elements is allocated.
A matrix has various a few properties
- Number of rows (gslmm::matrix<T>::row_size())
- Number of columns (gslmm::matrix<T>:columns_size())
 elements, where
elements, where  is the number of rows, and
is the number of rows, and  is the number of columns.
is the number of columns.
Vadrious operations are defined on matrices, including sub-views, retrivial of the diagonal, and super- and sub-diagonals.
Normal matrix-matrix, matrix-vector, and matrix-scalar operations are defined as well. If the matrices 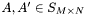 ,
,  ,
, 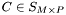 , and the vectors
, and the vectors 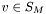 ,
,  , and the scalar
, and the scalar 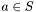 for some set of numbers
for some set of numbers 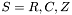 , then the following operations are defined
, then the following operations are defined

These operations are implemented via the corresponding global C++ operators ( operator*(const matrix<T>&,const double&), operator+(const matrix<T>&,const double&), operator*(const matrix<T>&,const vector<T>&), operator*(const matrix<T>&,const matrix<T>&)). For the matrix-vector and matrix-matrix product, the operators call the global functions matrix_vector_product and matrix_matrix_product respectively.
Note, that the global operators for 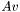 and
and  as well as their corresponding functions, do not return a new vector or matrix. Instead the return an object of a specialised class (_matrix_vector_mult for
as well as their corresponding functions, do not return a new vector or matrix. Instead the return an object of a specialised class (_matrix_vector_mult for 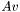 , and _matrix_matrix_mult for
, and _matrix_matrix_mult for  ). This is to allow for defered evaluation of the potentially expensive operation of
). This is to allow for defered evaluation of the potentially expensive operation of 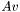 or
or  . (This follows the outline of section 22.4.7 of The C++ Programming Language (Special Edition) by Bjarne Stroustrup).
. (This follows the outline of section 22.4.7 of The C++ Programming Language (Special Edition) by Bjarne Stroustrup).
The special object simple contains references to the two operands of the operation. When a vector or matrix is assigned from this object, the operation is evaluated in-place - that is, without a temporary object. For example
size_t m=3, n=2, p=4; // 1: Dimension gslmm::matrix<double> A(m,n); // 2: Left-hand operand gslmm::matrix<double> B(n,p); // 3: Right-hand operand gslmm::matrix<double> C(m,p) // 4: To be assigned A * B fill_matrix(A); // 5: Set elements of A fill_matrix(B); // 6: Set elements of B C = A * B; // 7: Assign A * B to C
If the * operator was defined to return a new matrix, then in line 7 we could have potentially 2 useless temporaries:
- First, we would make a temporary
 in the
in the operator*function, and assign the elements . This would be one un-wanted construction.
. This would be one un-wanted construction. - Since we could not return a reference to this object, as it goes out of scope when leaving the
operator*function, we'd have to copy onto the return stack as
onto the return stack as  . That is, we'd do a copy construction for the return object
. That is, we'd do a copy construction for the return object  , and we'd destruct
, and we'd destruct  .
. - Finally, we would assign to
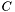 the elements of
the elements of  , and then destroy
, and then destroy 
That is, we'd have one un-wanted construction, one un-wanted copy construction, and to un-wanted destructions.
However, in the implementation used here, we construct a small special object in the operator* function, and copy that back on the return stack. Since the special object is small (two references to the operands), this is not a large overhead, and never depends on the size of the matrices and vectors involved. When the assignment operator is envoked in line 7 above, it takes care of evaluating the operation, and assign directly to the elements of 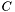 .
.
Note, that in the default definition of these operators, no tricks has been employed to speed up the calculation. To use better code for these operations, one should include the relevant Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS) headers. This makes even more sense when manipulators are used to flag properties of a matrix.
Matrix manipulators are functions that flags a matrix as having a certain property. For example
gslmm::matrix<double> A(3,3); // Matrix assign_matrix(A); // Make a symmetric matrix gslmm::symmetric(A); // Say that A is symmetric
 is a symmetric matrix,
is a symmetric matrix,
![\[ A = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} A_{00} & A_{01} & A_{02} \\ A_{01} & A_{11} & A_{12} \\ A_{02} & A_{12} & A_{22} \\ \end{array}\right) \]](form_826.png)
and that we should only reference the upper-right triangle of the matrix (the lower-left is the same as the upper-right).
The matrix manipulator functions return an object of matrix_manip<T>. The various operators are also definied for matrix manipulators, so one can do
matrix<double> A(...); matrix<double> B(...); matrix<double> C(...); C = gslmm::symmetrix(A) * B;
matrix<complex<double> > A(...); matrix<complex<double> > B(...); matrix<complex<double> > C(...); C = gslmm::transpose(gslmm::hermitian(A)) * B;
Whenever optimised BLAS algorithms exists, and the user has included the relevant BLAS headers, they are used.
Note, that operators operator+=, operator-=, operator*=, and operator/= are element-wise operations. If you think about it, you will see why. For example, suppose 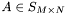 ,
,  ,
, 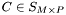 , and
, and  , then if the
, then if the operator*= function implemented  the code
the code
A *= B;
 to
to  . Changing the dimension of a matrix or vector is now allowed in GSL-- (nor GSL) because it can have very bad and unexpected side-effects.
. Changing the dimension of a matrix or vector is now allowed in GSL-- (nor GSL) because it can have very bad and unexpected side-effects.
Classes | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< char > |
Matrix char specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< complex< double > > |
Matrix complex<double> specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< double > |
Matrix double specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< float > |
Matrix float specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< int > |
Matrix int specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< long > |
Matrix long specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< long double > |
Matrix long double specialisation. More... | |
| struct | gslmm::_matrix_mult< T > |
| Class that represents a matrix-matrix product. More... | |
| struct | gslmm::_matrix_manip_mult< T > |
| Class that represents a matrix-matrix product. More... | |
| struct | gslmm::_matrix_vector_mult< T > |
| Class that represents a matrix-matrix product. More... | |
| struct | gslmm::_matrix_manip_vector_mult< T > |
| Class that represents a matrix-matrix product. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< short > |
Matrix short specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< unsigned char > |
Matrix unsigned char specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< unsigned int > |
Matrix unsigned int specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< unsigned long > |
Matrix unsigned long specialisation. More... | |
| class | gslmm::matrix< unsigned short > |
Matrix unsigned short specialisation. More... | |
| class | matrix |
| Base template for matricies classes. More... | |
| struct | gslmm::matrix_manip< T > |
| Manipulator of matrixes. More... | |
Matrix manipulator - enumerations | |
| enum | gslmm::type { gslmm::general_type, gslmm::triangular_type, gslmm::inverse_triangular_type, gslmm::symmetric_type, gslmm::hermitian_type } |
| enum | gslmm::transform { gslmm::no_transform = CblasNoTrans, gslmm::transpose_transform = CblasTrans, gslmm::adjoint_transform = CblasConjTrans } |
| enum | gslmm::location { gslmm::upper_triangle = CblasUpper, gslmm::lower_triangle = CblasLower } |
| enum | gslmm::diagonal { gslmm::non_unit_diagonal = CblasNonUnit, gslmm::unit_diagonal = CblasUnit } |
| enum | gslmm::side { gslmm::left_side = CblasLeft, gslmm::right_side = CblasRight } |
| enum | gslmm::order { gslmm::row_major = CblasRowMajor, gslmm::column_major = CblasColMajor } |
Matrix manipulator - triangular | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::triangular (Ref< T > r, location l=upper_triangle, diagonal d=non_unit_diagonal) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::triangular (matrix< T > &m, location l=upper_triangle, diagonal d=non_unit_diagonal) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > & | gslmm::triangular (matrix_manip< T > r, location l=upper_triangle, diagonal d=non_unit_diagonal) |
Matrix manipulator - triangular, inverse | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::inverse_triangular (Ref< T > r, location l=upper_triangle, diagonal d=non_unit_diagonal) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::inverse_triangular (matrix< T > &m, location l=upper_triangle, diagonal d=non_unit_diagonal) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > & | gslmm::inverse_triangular (matrix_manip< T > r, location l=upper_triangle, diagonal d=non_unit_diagonal) |
Matrix manipulator - symmetric | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::symmetric (Ref< T > r, location l=upper_triangle) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::symmetric (matrix< T > &m, location l=upper_triangle) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::symmetric (matrix_manip< T > r, location l=upper_triangle) |
Matrix manipulator - Hermitian | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::hermitian (Ref< T > r, location l=upper_triangle) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::hermitian (matrix< T > r, location l=upper_triangle) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::hermitian (matrix_manip< T > r, location l=upper_triangle) |
Matrix manipulator - transposition | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::transpose (Ref< T > r) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::transpose (matrix< T > &m) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::transpose (matrix_manip< T > r) |
Matrix manipulator - adjoint | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::adjoint (Ref< T > r) |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::adjoint (matrix< T > m) |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::adjoint (matrix_manip< T > r) |
Matrix manipulator - left-multiplication | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::left (Ref< T > r) |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::left (matrix< T > m) |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::left (matrix_manip< T > r) |
Matrix manipulator - right-multiplication | |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::right (Ref< T > r) |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::right (matrix< T > m) |
| template<typename T, template< class > class Ref> | |
| matrix_manip< T > | gslmm::right (matrix_manip< T > r) |
Matrix-matrix products | |
| template<typename Type> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const Type &alpha, const matrix< Type > &a, const matrix< Type > &b, const Type &beta, matrix< Type > &c) |
| template<typename Type> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const Type &alpha, const matrix_manip< Type > a, const matrix_manip< Type > b, const Type &beta, matrix< Type > &c) |
| template<typename Type> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const Type &alpha, const matrix_manip< Type > a, const matrix< Type > &b, const Type &beta, matrix< Type > &c) |
Matrix-vector products | |
| template<typename Type> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const Type &alpha, const matrix< Type > &a, const vector< Type > &v, const Type &beta, vector< Type > &u) |
| template<typename Type> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const Type &alpha, const matrix_manip< Type > a, const vector< Type > &v, const Type &beta, vector< Type > &u) |
General operations on matricies | |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator+ (const matrix< T > &lhs, const matrix< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator- (const matrix< T > &lhs, const matrix< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T> | |
| _matrix_mult< T > | gslmm::operator * (const matrix< T > &lhs, const matrix< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator/ (const matrix< T > &lhs, const matrix< T > &rhs) |
General operations on matrix-vector | |
| template<typename T> | |
| _matrix_vector_mult< T > | gslmm::operator * (const matrix< T > &lhs, const vector< T > &rhs) |
General operations on matrix-scaler | |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator+ (const matrix< T > &m, const double &a) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator- (const matrix< T > &m, const double &a) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator * (const matrix< T > &m, const double &a) |
| template<typename T> | |
| matrix< T > | gslmm::operator/ (const matrix< T > &m, const double &a) |
Operators on matrix manipulators | |
| template<typename T> | |
| _matrix_manip_mult< T > | gslmm::operator * (const matrix_manip< T > lhs, const matrix_manip< T > rhs) |
| template<typename T> | |
| _matrix_manip_mult< T > | gslmm::operator * (const matrix_manip< T > lhs, const matrix< T > &rhs) |
| template<typename T> | |
| _matrix_manip_vector_mult< T > | gslmm::operator * (const matrix_manip< T > lhs, const vector< T > &rhs) |
Functions | |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const complex< double > &alpha, const matrix< complex< double > > &a, const vector< complex< double > > &v, const complex< double > &beta, vector< complex< double > > &u) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const complex< double > &alpha, const matrix_manip< complex< double > > a, const vector< complex< double > > &v, const complex< double > &beta, vector< complex< double > > &u) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const complex< double > &alpha, const matrix< complex< double > > &a, const matrix< complex< double > > &b, const complex< double > &beta, matrix< complex< double > > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const complex< double > &alpha, const matrix_manip< complex< double > > a, const matrix_manip< complex< double > > b, const complex< double > &beta, matrix< complex< double > > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const complex< double > &alpha, const matrix_manip< complex< double > > a, const matrix< complex< double > > &b, const complex< double > &beta, matrix< complex< double > > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const double &alpha, const matrix< double > &a, const vector< double > &v, const double &beta, vector< double > &u) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const double &alpha, const matrix_manip< double > a, const vector< double > &v, const double &beta, vector< double > &u) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const double &alpha, const matrix< double > &a, const matrix< double > &b, const double &beta, matrix< double > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const double &alpha, const matrix_manip< double > a, const matrix_manip< double > b, const double &beta, matrix< double > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const double &alpha, const matrix_manip< double > a, const matrix< double > &b, const double &beta, matrix< double > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const float &alpha, const matrix< float > &a, const vector< float > &v, const float &beta, vector< float > &u) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_vector_product (const float &alpha, const matrix_manip< float > a, const vector< float > &v, const float &beta, vector< float > &u) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const float &alpha, const matrix< float > &a, const matrix< float > &b, const float &beta, matrix< float > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const float &alpha, const matrix_manip< float > a, const matrix_manip< float > b, const float &beta, matrix< float > &c) |
| template<> | |
| void | gslmm::matrix_matrix_product (const float &alpha, const matrix_manip< float > a, const matrix< float > &b, const float &beta, matrix< float > &c) |
Enumeration Type Documentation
|
|
Whether it is safe to assume that the diagnal is the unit matrix, or not.
That is, if
|
|
|
Storage of triangle matrix. Chooses where the matrix is stored: in the upper or lower triangle of the matrix. |
|
|
Order or matrices.
|
|
|
Order of the multiplication.
|
|
|
Operations on matrix passed to the routines.
|
|
|
Types of matrix.
|
Function Documentation
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should make a conjugate transpose operation on the matrix.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should make a conjugate transpose operation on the matrix.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should make a conjugate transpose operation on the matrix.
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is hermitian.
That is,
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is hermitian.
That is,
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is hermitian.
That is,
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is trianular, and that we should use it's inverse. That is, the matrix is of the form
and we should use the inverse of that.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is trianular, and that we should use it's inverse. That is, the matrix is of the form
and we should use the inverse of that.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is trianular, and that we should use it's inverse. That is, the matrix is of the form
and we should use the inverse of that.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should do left hand side multiplication.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should do left hand side multiplication.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should do left hand side multiplication.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product of manipulated matrices.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product of manipulated matrices.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compute the matrix-matrix product.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
compute the matrix-vector product and sum
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
* operation between a manipulator of matrix and a vector This is implemented straight forwardly. No hanky-panky here.
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
* operation between manipulators of matrices This is implemented straight forwardly. No hanky-panky here.
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
* operation between manipulators of matrices This is implemented straight forwardly. No hanky-panky here.
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
* operation between matrix and number (element by element)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
* operation between a matrix and a vector This is implemented straight forwardly.
No hanky-panky here. If the BLAS headers are included, then the BLAS function gslmm::matrix_vector_product will be used for those types it's defined for (
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
* operation between matricies This is implemented straight forwardly.
No hanky-panky here. If the BLAS headers are included, then the BLAS function gslmm::matrix_matrix_product will be used for those types it's defined for (
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
+ operation between matrix and number (element by element)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
+ operation between matricies (element by element)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
/ operation between matrix and number (element by element)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
/ operation between matricies This is generally not defined.
It will simply return a copy of lhs (division by identity :-) If the linear algebra header (gslmm/linear/linear.hh) is included, then this is implemented using decompositions for a subset of the available types (all sorts of matrices of
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should do right hand side multiplication.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should do right hand side multiplication.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should do right hand side multiplication.
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is symmetric.
That is,
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is symmetric.
That is,
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is symmetric.
That is,
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should make a transpose operation on the matrix.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should make a transpose operation on the matrix.
|
|
||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says we should make a transpose operation on the matrix.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is triangular. That is, it is of the form
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is triangular. That is, it is of the form
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Matrix manipulation that says the matrix is trianular. That is, it is of the form
|
| Top of page | Last update Tue May 9 10:11:29 2006 |
| Christian
Holm |
Created by DoxyGen 1.4.6 |
![\[ \left(\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & & \\ & 1 & \\ & & \ddots \\ \end{array}\right) \]](form_0.png)
 .
. 
![\[ \left(\begin{array}{ccc} x & x & x \\ & x & x \\ & & x \\ \end{array}\right) \]](form_1.png)
 .
. 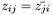 .
.  .
.![\[ \left(\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & x & x \\ & 1 & x \\ & & 1 \\ \end{array}\right) \]](form_2.png)










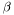


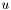 , which is overwritten on output by the matrix-vector product.
, which is overwritten on output by the matrix-vector product. 
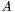





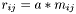
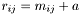





 .
.