
Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-PAS-FTR-18-016 | ||
| Search for invisible decays of a Higgs boson produced through vector boson fusion at the High-Luminosity LHC | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| November 2018 | ||
| Abstract: The search for a Higgs boson decaying to invisible particles, produced through the vector boson fusion mode in the High-Luminosity LHC proton-proton collisions at $\sqrt{s}= $ 14 TeV, is investigated based on simulation studies using Delphes, a fast-simulation package used to provide a parameterised response of the upgraded CMS detector. The event selection follows the existing CMS Run II data analysis, optimised for the High-Luminosity LHC conditions. The 95% confidence-level upper limits on the branching fraction of a standard-model-like Higgs boson decaying to invisible final states are studied with integrated luminosities of 300, 1000 and 3000 fb$^{-1}$ as a function of the thresholds applied on the transverse energy of the recoiling Higgs boson deposited in the detector. | ||
| Links: CDS record (PDF) ; inSPIRE record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
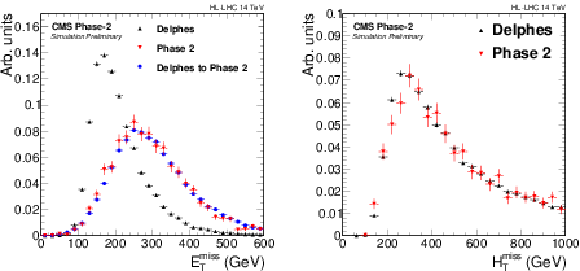
Figure 1:
$ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ (left) and $ {\mathrm {H}_{\mathrm {T}}^{\mathrm {miss}}} $ (right) distributions in 200 PU VBF H signal samples, comparing full simulation (Phase 2) and Delphes. On the left, the distribution in Delphes is smeared as explained in the main text to reproduce the Phase 2 distribution. |
png pdf |
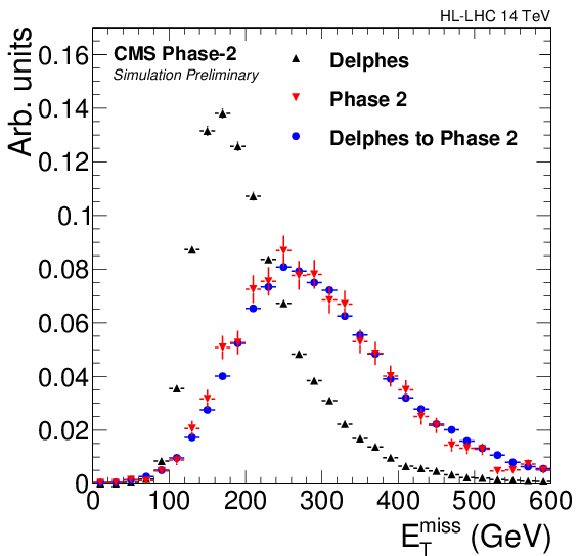
Figure 1-a:
$ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ (left) and $ {\mathrm {H}_{\mathrm {T}}^{\mathrm {miss}}} $ (right) distributions in 200 PU VBF H signal samples, comparing full simulation (Phase 2) and Delphes. On the left, the distribution in Delphes is smeared as explained in the main text to reproduce the Phase 2 distribution. |

png pdf |
Figure 1-b:
$ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ (left) and $ {\mathrm {H}_{\mathrm {T}}^{\mathrm {miss}}} $ (right) distributions in 200 PU VBF H signal samples, comparing full simulation (Phase 2) and Delphes. On the left, the distribution in Delphes is smeared as explained in the main text to reproduce the Phase 2 distribution. |
png pdf |
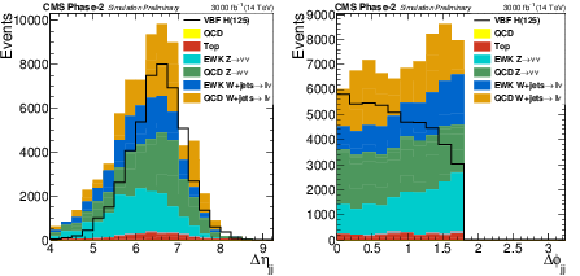
Figure 2:
Distributions of $|\Delta \eta _{\text {jj}}|$ and $|\Delta \phi _{\text {jj}}|$ in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |
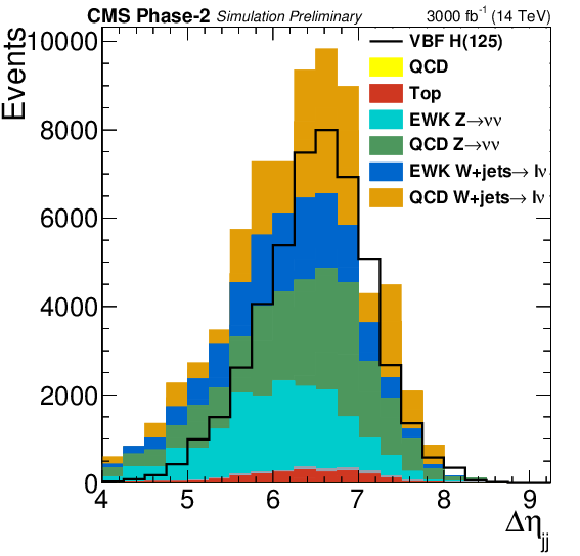
png pdf |
Figure 2-a:
Distributions of $|\Delta \eta _{\text {jj}}|$ and $|\Delta \phi _{\text {jj}}|$ in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |

png pdf |
Figure 2-b:
Distributions of $|\Delta \eta _{\text {jj}}|$ and $|\Delta \phi _{\text {jj}}|$ in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |
png pdf |
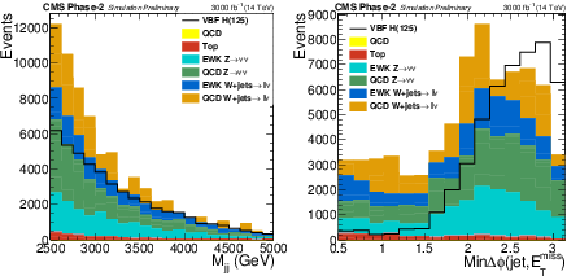
Figure 3:
Distributions of $M_{\text {jj}}$ and min$\Delta \phi $(jet $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} > $ 30 GeV, $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $) in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |
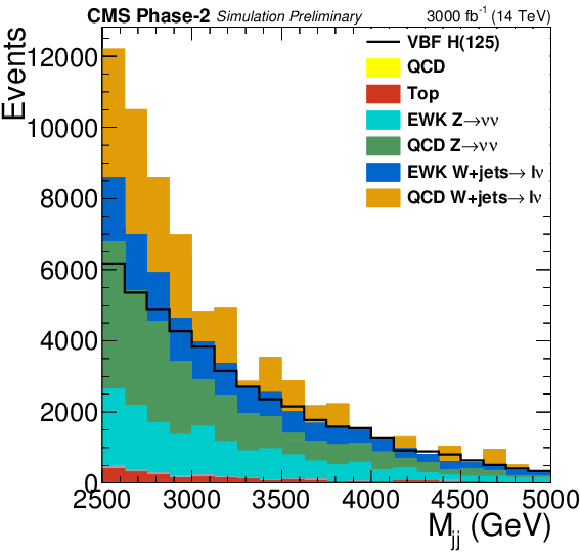
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
Distributions of $M_{\text {jj}}$ and min$\Delta \phi $(jet $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} > $ 30 GeV, $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $) in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |
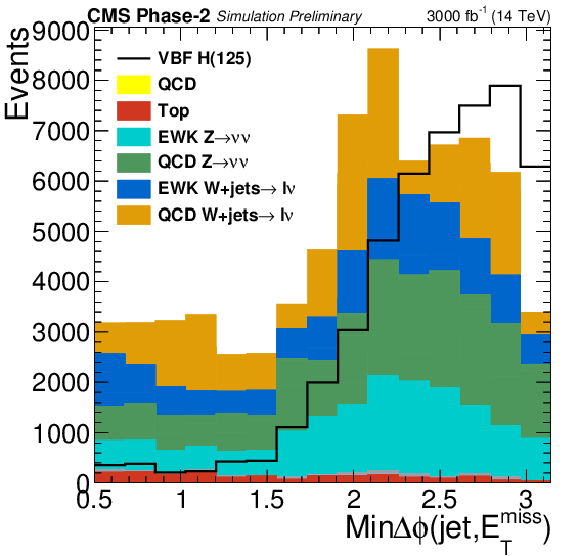
png pdf |
Figure 3-b:
Distributions of $M_{\text {jj}}$ and min$\Delta \phi $(jet $ {p_{\mathrm {T}}} > $ 30 GeV, $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $) in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |
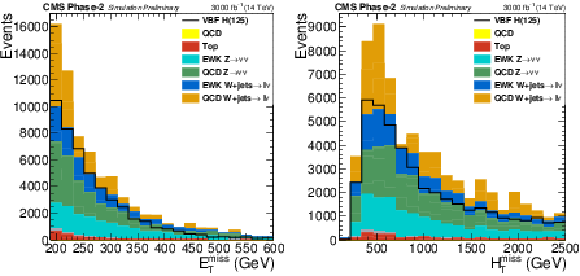
png pdf |
Figure 4:
Distributions of $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ and $ {\mathrm {H}_{\mathrm {T}}^{\mathrm {miss}}} $ in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |

png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
Distributions of $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ and $ {\mathrm {H}_{\mathrm {T}}^{\mathrm {miss}}} $ in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |
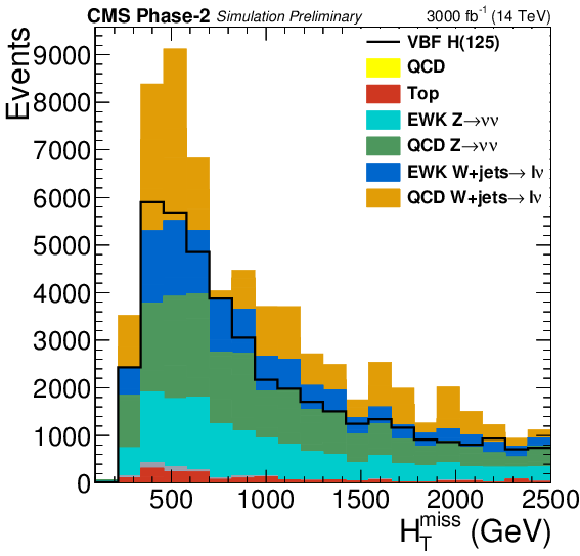
png pdf |
Figure 4-b:
Distributions of $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $ and $ {\mathrm {H}_{\mathrm {T}}^{\mathrm {miss}}} $ in the signal region for the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV. |

png pdf |
Figure 5:
Left: 95% CL limits on ${\text {B}({\mathrm {H}} \to \text {inv.})}$ as a function of the minimum threshold on $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $, for $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and an integrated luminosity of 3000 fb$^{-1}$. Right: 95% CL limits for scenarios with different integrated luminosities. |
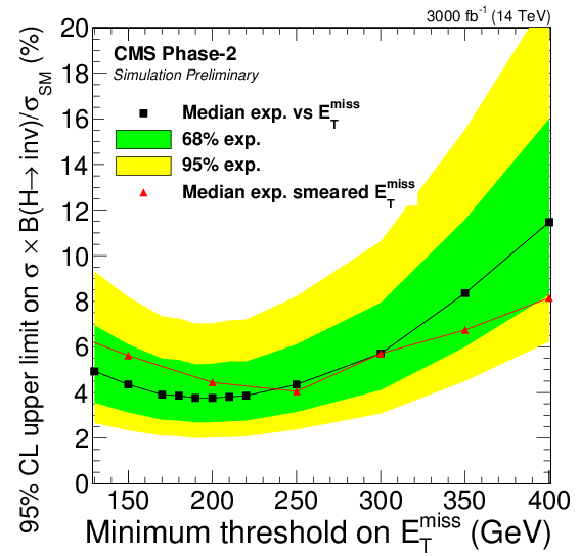
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
Left: 95% CL limits on ${\text {B}({\mathrm {H}} \to \text {inv.})}$ as a function of the minimum threshold on $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $, for $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and an integrated luminosity of 3000 fb$^{-1}$. Right: 95% CL limits for scenarios with different integrated luminosities. |
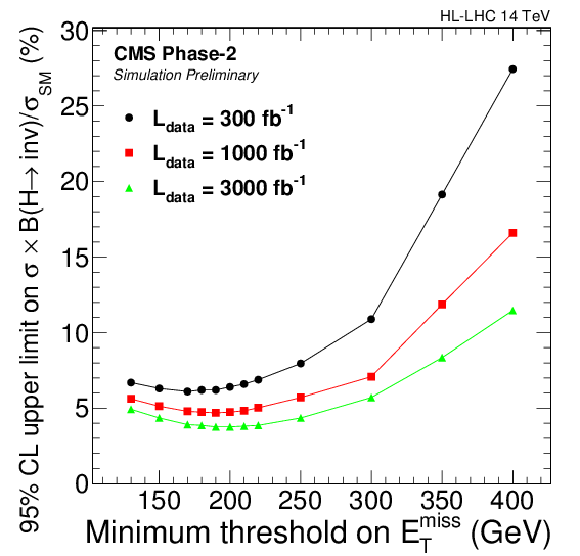
png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
Left: 95% CL limits on ${\text {B}({\mathrm {H}} \to \text {inv.})}$ as a function of the minimum threshold on $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} $, for $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and an integrated luminosity of 3000 fb$^{-1}$. Right: 95% CL limits for scenarios with different integrated luminosities. |
| Tables | |

png pdf |
Table 1:
Impact on the signal and background yields from the different sources of systematic uncertainty considered in Ref. [14] and for the HL-LHC setup considered in this analysis. |

png pdf |
Table 2:
Number of events expected after the final selection, $M_{\text {jj}} > $ 2500 GeV and $ {E_{\mathrm {T}}^{\text {miss}}} > $ 190 GeV, with an integrated luminosity of 3000 fb$^{-1}$. The uncertainties are the statistical uncertainties from the Delphes samples. |
| Summary |
| The search for a Higgs boson decaying invisibly, produced in the vector-boson fusion mode, is investigated at the HL-LHC through simulation studies using a fast parametrisation of the upgraded CMS detector. The analysis follows the latest CMS publication, with an event selection optimised for the HL-LHC conditions. The expected 95% CL upper limits on the branching ratio of the standard model Higgs boson to invisible particles are presented as a function of the lower threshold applied on the transverse missing energy, for scenarios with integrated luminosities of 300, 1000 and 3000 fb$^{-1}$. The 95% CL upper limit on $ {\text{B}(\mathrm{H}\to \text{inv.})} $ assuming standard model production is expected to be at 3.8%, for thresholds values of 2500 GeV (190 GeV) on the dijet mass (missing transverse momentum). Even if the transverse missing energy resolution is degraded by a factor of two due to the high pileup conditions, a similar sensitivity is nevertheless achieved. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of a new particle in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 1 | 1207.7214 |
| 2 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson at a mass of 125 GeV with the CMS experiment at the LHC | PLB 716 (2012) 30 | CMS-HIG-12-028 1207.7235 |
| 3 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of a new boson with mass near 125 GeV in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 06 (2013) 081 | CMS-HIG-12-036 1303.4571 |
| 4 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations | Measurements of the Higgs boson production and decay rates and constraints on its couplings from a combined ATLAS and CMS analysis of the LHC $ pp $ collision data at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 and 8 TeV | JHEP 08 (2016) 45 | 1606.02266 |
| 5 | R. E. Shrock and M. Suzuki | Invisible decays of Higgs bosons | Phy. Lett. B 110 (1982) 250 | |
| 6 | S. Baek, P. Ko, W.-I. Park, and E. Senaha | Higgs portal vector dark matter: revisited | JHEP 05 (2013) 036 | 1212.2131 |
| 7 | A. Djouadi, O. Lebedev, Y. Mambrini, and J. Quevillon | Implications of LHC searches for Higgs--portal dark matter | PLB 709 (2012) 65 | 1112.3299 |
| 8 | A. Djouadi, A. Falkowski, Y. Mambrini, and J. Quevillon | Direct detection of Higgs-portal dark matter at the LHC | EPJC 73 (2013) 2455 | 1205.3169 |
| 9 | ATLAS Collaboration | Constraints on new phenomena via Higgs boson couplings and invisible decays with the ATLAS detector | JHEP 11 (2015) 206 | 1509.00672 |
| 10 | ATLAS Collaboration | Search for invisible Higgs boson decays in vector boson fusion at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector | Submitted to: PL(2018) | 1809.06682 |
| 11 | CMS Collaboration | Searches for invisible decays of the Higgs boson in $ {{\mathrm{p}}{\mathrm{p}}} $ collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 7 , 8, and 13 TeV | JHEP 02 (2017) 135 | CMS-HIG-16-016 1610.09218 |
| 12 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in events with a leptonically decaying $ {\mathrm{Z}} $ boson and a large transverse momentum imbalance in proton-proton collisions at $ {\sqrt{s} = 13 TeV} $ | EPJC 78 (2018) 291 | CMS-EXO-16-052 1711.00431 |
| 13 | CMS Collaboration | Search for new physics in final states with an energetic jet or a hadronically decaying $ {\mathrm{W}} $ or $ {\mathrm{Z}} $ boson and transverse momentum imbalance at $ {\sqrt{s}=13 TeV} $ | PRD 97 (2018) 092005 | CMS-EXO-16-048 1712.02345 |
| 14 | CMS Collaboration | Search for invisible decays of a Higgs boson produced through vector boson fusion in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | Submitted to: PL(2018) | CMS-HIG-17-023 1809.05937 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Projected performance of higgs analyses at the hl-lhc for ecfa 2016 | CMS-PAS-FTR-16-002 | CMS-PAS-FTR-16-002 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS Experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Technical Proposal for the Phase-II Upgrade of the CMS Detector | CMS-PAS-TDR-15-002 | CMS-PAS-TDR-15-002 |
| 18 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Tracker | CDS | |
| 19 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Barrel Calorimeters Technical Design Report | CDS | |
| 20 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Endcap Calorimeter | CDS | |
| 21 | CMS Collaboration | The Phase-2 Upgrade of the CMS Muon Detectors | CDS | |
| 22 | CMS Collaboration | CMS Phase-2 Object Performance | ||
| 23 | DELPHES 3 Collaboration | DELPHES 3, A modular framework for fast simulation of a generic collider experiment | JHEP 02 (2014) 057 | 1307.6346 |
| 24 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4: A Simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 25 | J. Allison et al. | Geant4 developments and applications | IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53 (2006) 270 | |
| 26 | S. Alioli, P. Nason, C. Oleari, and E. Re | A general framework for implementing NLO calculations in shower monte carlo programs: the POWHEG BOX | JHEP 06 (2010) 043 | 1002.2581 |
| 27 | P. Nason and C. Oleari | NLO higgs boson production via vector-boson fusion matched with shower in POWHEG | JHEP 02 (2010) 037 | 0911.5299 |
| 28 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group | Handbook of LHC Higgs cross sections: 4. Deciphering the nature of the Higgs sector | 1610.07922 | |
| 29 | J. Alwall et al. | The automated computation of tree-level and next-to-leading order differential cross sections, and their matching to parton shower simulations | JHEP 07 (2014) 079 | 1405.0301 |
| 30 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti--$ {k_{\mathrm{T}}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 31 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 32 | D. Bertolini, P. Harris, M. Low, and N. Tran | Pileup Per Particle Identification | JHEP 10 (2014) 059 | 1407.6013 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) | |
| 34 | G. Cowan, K. Cranmer, E. Gross, and O. Vitells | Asymptotic formulae for likelihood-based tests of new physics | EPJC71 (2011) 1554 | 1007.1727 |
| 35 | A. L. Read | Presentation of search results: the $ cl_{s} $ technique | JPG 28 (2002) 2693 | |
| 36 | T. Junk | Confidence level computation for combining searches with small statistics | NIMA 434 (1999) 435 | |
| 37 | LHC Higgs Cross Section Working Group, S. Dittmaier et al. | Handbook of LHC Higgs Cross Sections: 2. Differential Distributions | CERN-2012-002 | 1201.3084 |
| 38 | ATLAS and CMS Collaborations, LHC Higgs Combination Group | Procedure for the LHC higgs boson search combination in Summer 2011 | ATL-PHYS-PUB-2011-11, CMS NOTE 2011/005 | |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|
|
|
|
|

|