
Compact Muon Solenoid
LHC, CERN
| CMS-HIN-19-004 ; CERN-EP-2022-036 | ||
| Strange hadron collectivity in pPb and PbPb collisions | ||
| CMS Collaboration | ||
| 29 April 2022 | ||
| JHEP 05 (2023) 007 | ||
| Abstract: The collective behavior of ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ and $\Lambda$/$\overline{\Lambda}$ strange hadrons is studied by measuring the elliptic azimuthal anisotropy ($v_2$) using the scalar-product and multiparticle correlation methods. Proton-lead (pPb) collisions at a nucleon-nucleon center-of-mass energy ${\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV and lead-lead (PbPb) collisions at ${\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV collected by the CMS experiment at the LHC are investigated. Nonflow effects in the pPb collisions are studied by using a subevent cumulant analysis and by excluding events where a jet with transverse momentum greater than 20 GeV is present. The strange hadron $v_2$ values extracted in pPb collisions via the four- and six-particle correlation method are found to be nearly identical, suggesting the collective behavior. Comparisons of the pPb and PbPb results for both strange hadrons and charged particles illustrate how event-by-event flow fluctuations depend on the system size. | ||
| Links: e-print arXiv:2205.00080 [hep-ex] (PDF) ; CDS record ; inSPIRE record ; HepData record ; CADI line (restricted) ; | ||
| Figures | |
png pdf |
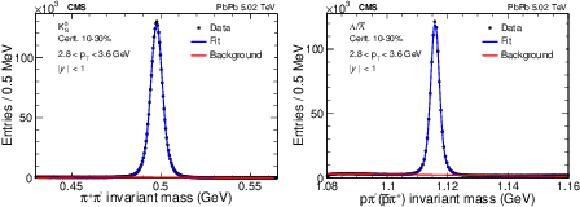
Figure 1:
Invariant mass distributions of ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons (left) and $\Lambda$ baryons (right) candidates within $ {| y |} <$ 1 and 2.8 $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} < $ 3.6 GeV in 10-30% centrality PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. The blue lines show the fitted signal peak. The red lines indicate the fitted background component. |
png pdf |
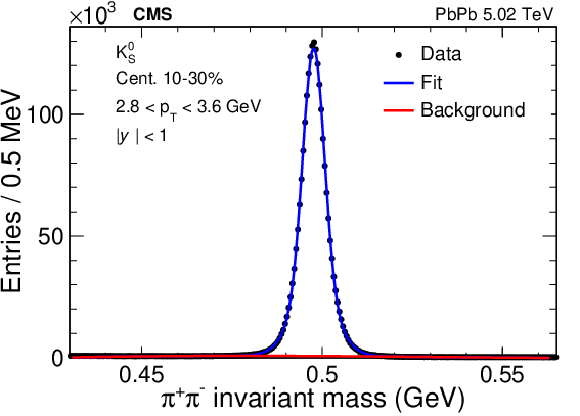
Figure 1-a:
Invariant mass distribution of ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ meson candidates within $ {| y |} <$ 1 and 2.8 $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} < $ 3.6 GeV in 10-30% centrality PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. The blue lines show the fitted signal peak. The red lines indicate the fitted background component. |
png pdf |
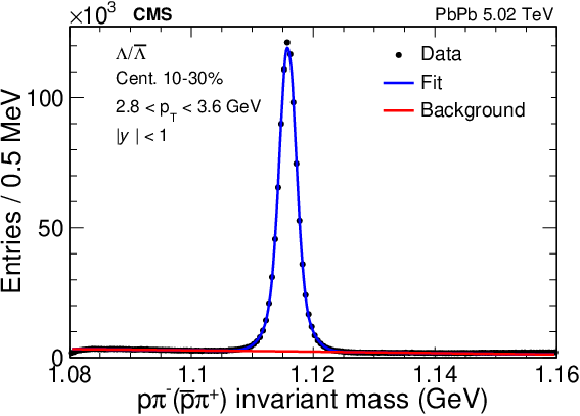
Figure 1-b:
Invariant mass distribution of $\Lambda$ baryon candidates within $ {| y |} <$ 1 and 2.8 $ < {p_{\mathrm {T}}} < $ 3.6 GeV in 10-30% centrality PbPb collisions at 5.02 TeV. The blue lines show the fitted signal peak. The red lines indicate the fitted background component. |
png pdf |
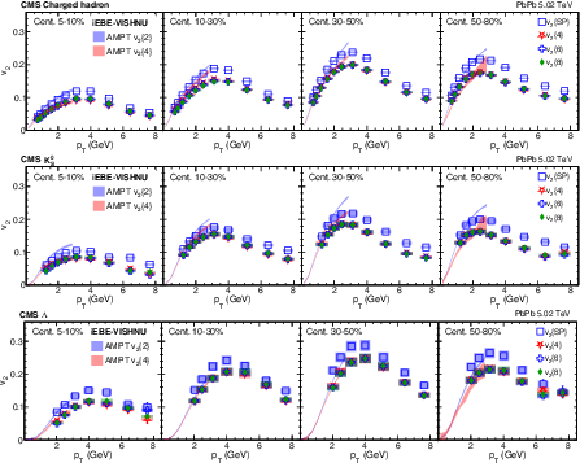
Figure 2:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for charged hadrons (upper), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons (middle), and $\Lambda$ baryons (lower) in different centrality intervals. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2\{2\}$ and $v_2\{4\}$ values with AMPT initial conditions. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
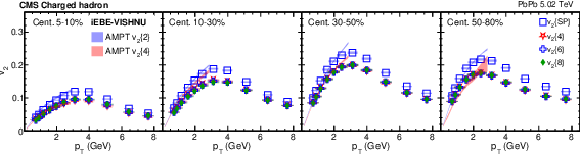
Figure 2-a:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for charged hadrons in different centrality intervals. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2\{2\}$ and $v_2\{4\}$ values with AMPT initial conditions. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
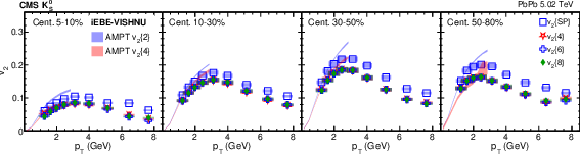
Figure 2-b:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons in different centrality intervals. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2\{2\}$ and $v_2\{4\}$ values with AMPT initial conditions. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
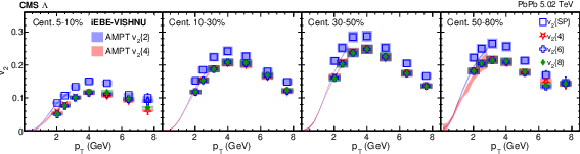
Figure 2-c:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for $\Lambda$ baryons in different centrality intervals. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2\{2\}$ and $v_2\{4\}$ values with AMPT initial conditions. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
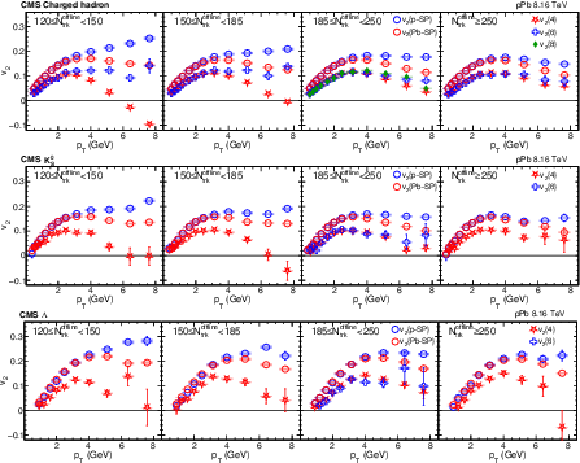
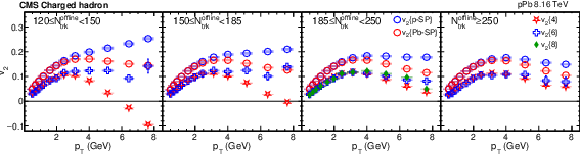
Figure 3:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for charged hadrons (upper), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons (middle), and $\Lambda$ baryons (lower) in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The scalar-product results are based on Q-vectors that are determined in either the p-going (p-SP) or Pb-going (Pb-SP) side HF calorimeter. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 3-a:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for charged hadrons in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The scalar-product results are based on Q-vectors that are determined in either the p-going (p-SP) or Pb-going (Pb-SP) side HF calorimeter. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
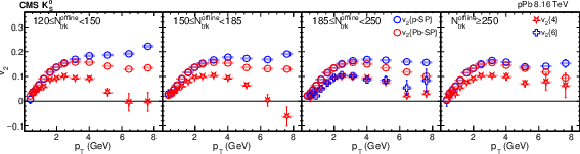
Figure 3-b:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The scalar-product results are based on Q-vectors that are determined in either the p-going (p-SP) or Pb-going (Pb-SP) side HF calorimeter. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
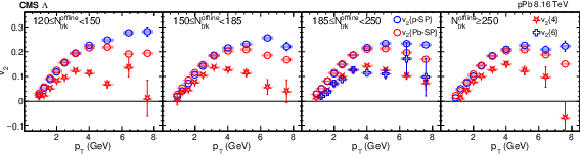
Figure 3-c:
The scalar-product and multiparticle cumulant $v_2$ results of pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for $\Lambda$ baryons in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The scalar-product results are based on Q-vectors that are determined in either the p-going (p-SP) or Pb-going (Pb-SP) side HF calorimeter. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
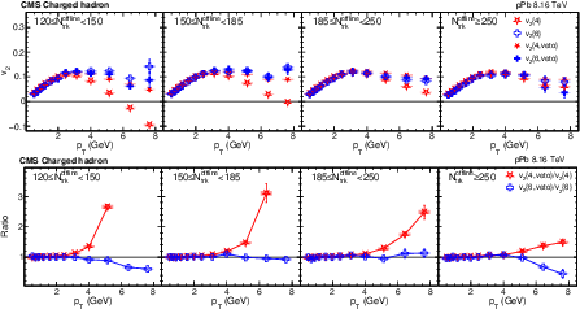
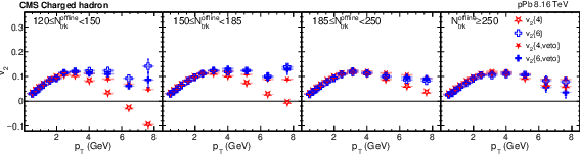
Figure 4:
The charged-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ distributions for pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with and without rejecting jet events (upper) and their ratios (lower) in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 4-a:
The charged-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ distributions for pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with and without rejecting jet events in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
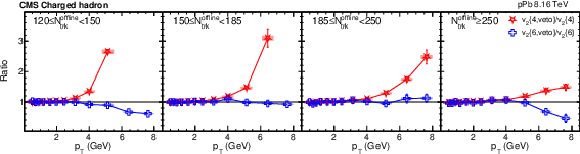
Figure 4-b:
Ratio of the charged-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and $v_2\{6\}$ distributions for pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with and without rejecting jet events in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
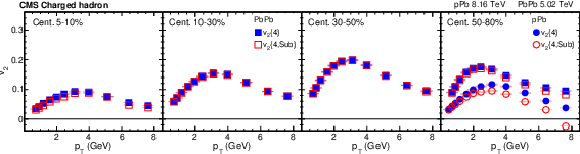
Figure 5:
The standard 4-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and subevent 4-particle ${v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}}$ values from PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for charged hadrons (upper), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons (middle), and $\Lambda$ baryons (lower) in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
png pdf |
Figure 5-a:
The standard 4-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and subevent 4-particle ${v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}}$ values from PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for charged hadrons in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
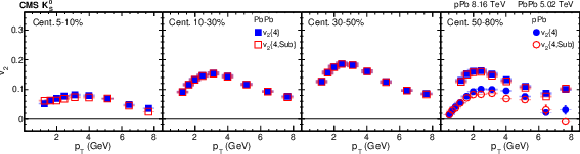
png pdf |
Figure 5-b:
The standard 4-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and subevent 4-particle ${v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}}$ values from PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
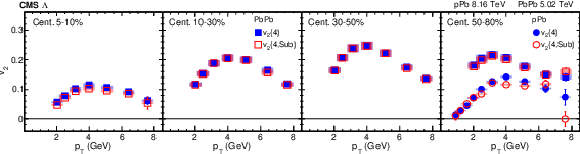
png pdf |
Figure 5-c:
The standard 4-particle $v_2\{4\}$ and subevent 4-particle ${v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}}$ values from PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for $\Lambda$ baryons in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 6:
The $v_2\{4\}$ and ${v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}}$ values from pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for charged hadrons in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 7:
The $ {v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}} /v_2\{4\}$ ratios for charged hadrons, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons and $\Lambda$ baryons, for PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV in different centrality intervals (upper) and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges (lower). The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
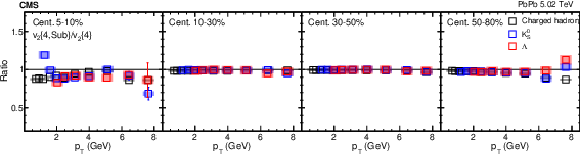
png pdf |
Figure 7-a:
The $ {v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}} /v_2\{4\}$ ratios for charged hadrons, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons and $\Lambda$ baryons, for PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
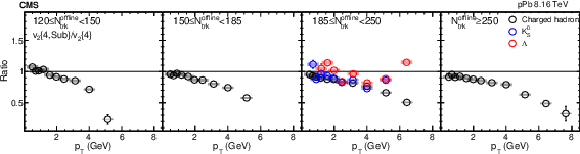
png pdf |
Figure 7-b:
The $ {v_2\{4,\text {Sub}\}} /v_2\{4\}$ ratios for charged hadrons, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons and $\Lambda$ baryons, for pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
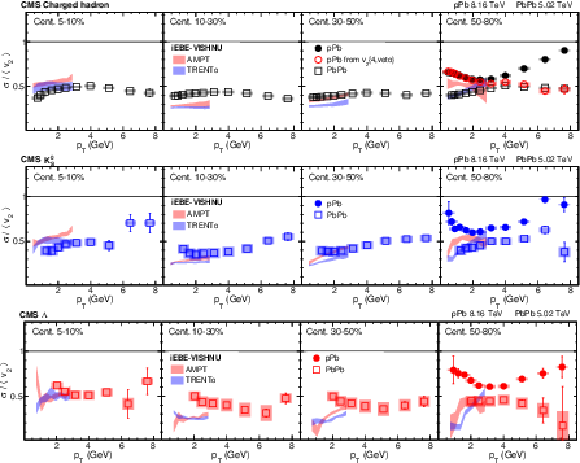
png pdf |
Figure 8:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results for PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV in different centrality intervals and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with 185 $\le {N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}} <$ 250 using $v_2\{\text {Pb-SP}\}$ for charged hadrons (upper), ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons (middle), and $\Lambda$ baryons (lower). The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with AMPT and TRENTo initial conditions in PbPb collisions [64]. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
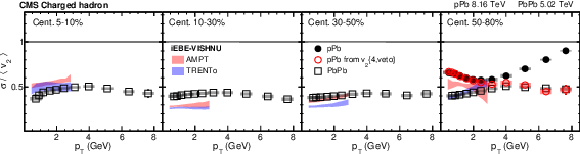
png pdf |
Figure 8-a:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results for PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV in different centrality intervals and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with 185 $\le {N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}} <$ 250 using $v_2\{\text {Pb-SP}\}$ for charged hadrons. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with AMPT and TRENTo initial conditions in PbPb collisions [64]. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
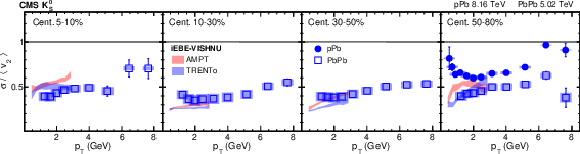
png pdf |
Figure 8-b:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results for PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV in different centrality intervals and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with 185 $\le {N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}} <$ 250 using $v_2\{\text {Pb-SP}\}$ for ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with AMPT and TRENTo initial conditions in PbPb collisions [64]. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |

png pdf |
Figure 8-c:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results for PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV in different centrality intervals and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV with 185 $\le {N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}} <$ 250 using $v_2\{\text {Pb-SP}\}$ for $\Lambda$ baryons. The shaded bands are hydrodynamic calculations of $v_2$ fluctuations with AMPT and TRENTo initial conditions in PbPb collisions [64]. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
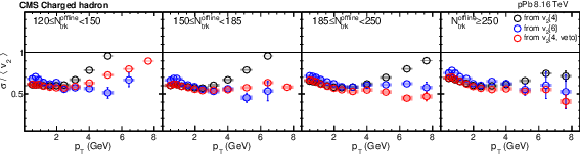
png pdf |
Figure 9:
The $v_2$ fluctuation results of pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV for charged hadrons derived from different multiparticle correlations in different ${N_\text {trk}^\text {offline}}$ ranges. The vertical bars and shaded boxes show the statistical and systematic uncertainties. |
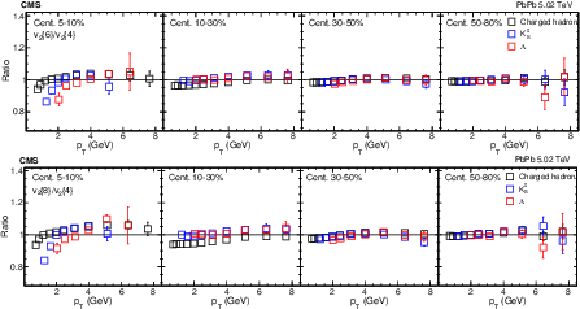
png pdf |
Figure 10:
The $v_2\{6\}/v_2\{4\}$ (upper) and $v_2\{8\}/v_2\{4\}$ (lower) ratios in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for charged hadrons, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons, and $\Lambda$ baryons in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars show the statistical uncertainties. The uncertainties are treated as uncorrelated for the ratios. |
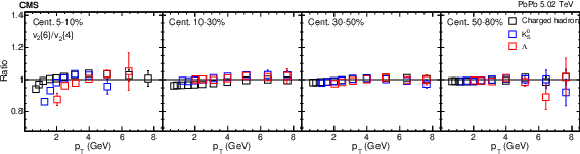
png pdf |
Figure 10-a:
The $v_2\{6\}/v_2\{4\}$ ratio in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for charged hadrons, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons, and $\Lambda$ baryons in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars show the statistical uncertainties. The uncertainties are treated as uncorrelated for the ratios. |

png pdf |
Figure 10-b:
The $v_2\{8\}/v_2\{4\}$ ratio in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV for charged hadrons, ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons, and $\Lambda$ baryons in different centrality intervals. The vertical bars show the statistical uncertainties. The uncertainties are treated as uncorrelated for the ratios. |
| Summary |
|
The elliptic azimuthal anisotropy $v_2$ values have been measured using the scalar-product and the multiparticle $Q$-cumulant methods for ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons, $\Lambda$ baryons, and charged hadrons in lead-lead (PbPb) collisions at ${\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV and high-multiplicity proton-lead (pPb) collisions at ${\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV. For the first time, multiparticle correlations of identified strange particles have been studied for pPb collisions. The hydrodynamic model calculations of scalar-product $v_2\{\text{SP}\}$ and 4-particle $v_2\{4\}$ values for ${\mathrm{K^0_S}}$ mesons, $\Lambda$ baryons and charged hadrons using different initial conditions are found to be qualitatively consistent with the observations in PbPb collisions. No obvious particle species dependence of the fluctuations in the $v_2$ values is observed for either the PbPb or pPb systems, indicating an origin of observed $v_2$ fluctuations from the initial-state geometry. The flow fluctuations are observed to be larger in pPb collisions at low transverse momentum (${p_{\mathrm{T}}}$). However, once jet correlations are removed, the pPb fluctuations are similar to those observed in peripheral PbPb collisions at high ${p_{\mathrm{T}}}$. Nonflow effects are studied for the multiparticle cumulant results. A large difference between the 4- and 6-particle $v_2$ values in pPb collisions that is not present for PbPb collisions can be explained by jet-related correlations. These nonflow correlations are suppressed by rejecting events with at least one jet with ${p_{\mathrm{T}}} > $ 20 GeV. A subevent cumulant method is also performed to reduce short-range correlation effects in pPb and PbPb collisions. Whereas the jet rejection study results in higher values for $v_2\{4\}$ as compared to the standard method, the subevent method leads to smaller values. This difference may be attributed to the effect of flow decorrelations on the subevent cumulant method. |
| References | ||||
| 1 | STAR Collaboration | Disappearance of back-to-back high $ {p_{\mathrm{T}}} $ hadron correlations in central AuAu collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 90 (2003) 082302 | nucl-ex/0210033 |
| 2 | PHENIX Collaboration | Elliptic flow of identified hadrons in AuAu collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 91 (2003) 182301 | nucl-ex/0305013 |
| 3 | PHOBOS Collaboration | System size, energy, pseudorapidity, and centrality dependence of elliptic flow | PRL 98 (2007) 242302 | nucl-ex/0610037 |
| 4 | CMS Collaboration | Long-range and short-range dihadron angular correlations in central PbPb collisions at a nucleon-nucleon center of mass energy of 2.76 TeV | JHEP 07 (2011) 076 | CMS-HIN-11-001 1105.2438 |
| 5 | CMS Collaboration | Centrality dependence of dihadron correlations and azimuthal anisotropy harmonics in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | EPJC 72 (2012) 2012 | CMS-HIN-11-006 1201.3158 |
| 6 | ALICE Collaboration | Elliptic flow of charged particles in PbPb collisions at 2.76 TeV | PRL 105 (2010) 252302 | 1011.3914 |
| 7 | ATLAS Collaboration | Measurement of the azimuthal anisotropy for charged particle production in $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV lead-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRC 86 (2012) 014907 | 1203.3087 |
| 8 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of the elliptic anisotropy of charged particles produced in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | PRC 87 (2013) 014902 | CMS-HIN-10-002 1204.1409 |
| 9 | CMS Collaboration | Studies of azimuthal dihadron correlations in ultra-central PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | JHEP 02 (2014) 088 | CMS-HIN-12-011 1312.1845 |
| 10 | J.-Y. Ollitrault | Anisotropy as a signature of transverse collective flow | PRD 46 (1992) 229 | |
| 11 | U. Heinz and R. Snellings | Collective flow and viscosity in relativistic heavy-ion collisions | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 63 (2013) 123 | 1301.2826 |
| 12 | C. Gale, S. Jeon, and B. Schenke | Hydrodynamic modeling of heavy-ion collisions | Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 28 (2013) 1340011 | 1301.5893 |
| 13 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of long-range near-side angular correlations in proton-proton collisions at the LHC | JHEP 09 (2010) 091 | CMS-QCD-10-002 1009.4122 |
| 14 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of long-range elliptic azimuthal anisotropies in $ \sqrt{s}= $ 13 and 2.76 TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRL 116 (2016) 172301 | 1509.04776 |
| 15 | CMS Collaboration | Measurement of long-range near-side two-particle angular correlations in pp collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | PRL 116 (2016) 172302 | CMS-FSQ-15-002 1510.03068 |
| 16 | CMS Collaboration | Evidence for collectivity in pp collisions at the LHC | PLB 765 (2017) 193 | CMS-HIN-16-010 1606.06198 |
| 17 | CMS Collaboration | Observation of long-range near-side angular correlations in proton-lead collisions at the LHC | PLB 718 (2013) 795 | CMS-HIN-12-015 1210.5482 |
| 18 | ALICE Collaboration | Long-range angular correlations on the near and away side in pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | PLB 719 (2013) 29 | 1212.2001 |
| 19 | ATLAS Collaboration | Observation of associated near-side and away-side long-range correlations in $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV proton-lead collisions with the ATLAS detector | PRL 110 (2013) 182302 | 1212.5198 |
| 20 | LHCb Collaboration | Measurements of long-range near-side angular correlations in $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5 TeV proton-lead collisions in the forward region | PLB 762 (2016) 473 | 1512.00439 |
| 21 | PHENIX Collaboration | Measurement of long-range angular correlation and quadrupole anisotropy of pions and (anti)protons in central d+Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 114 (2015) 192301 | 1404.7461 |
| 22 | STAR Collaboration | Long-range pseudorapidity dihadron correlations in d+Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PLB 747 (2015) 265 | 1502.07652 |
| 23 | PHENIX Collaboration | Measurements of elliptic and triangular flow in high-multiplicity $ ^{3} $He$ + $Au collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 200 GeV | PRL 115 (2015) 142301 | 1507.06273 |
| 24 | S. Voloshin and Y. Zhang | Flow study in relativistic nuclear collisions by Fourier expansion of azimuthal particle distributions | Z. Phys. C 70 (1996) 665 | hep-ph/9407282 |
| 25 | B. H. Alver, C. Gombeaud, M. Luzum, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Triangular flow in hydrodynamics and transport theory | PRC 82 (2010) 034913 | 1007.5469 |
| 26 | B. Schenke, S. Jeon, and C. Gale | Elliptic and triangular flow in event-by-event (3+1)D viscous hydrodynamics | PRL 106 (2011) 042301 | 1009.3244 |
| 27 | Z. Qiu, C. Shen, and U. Heinz | Hydrodynamic elliptic and triangular flow in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | PLB 707 (2012) 151 | 1110.3033 |
| 28 | J. L. Nagle and W. A. Zajc | Small system collectivity in relativistic hadronic and nuclear collisions | Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 68 (2018) 211 | 1801.03477 |
| 29 | K. Dusling and R. Venugopalan | Comparison of the color glass condensate to dihadron correlations in proton-proton and proton-nucleus collisions | PRD 87 (2013) 094034 | 1302.7018 |
| 30 | K. Dusling, M. Mace, and R. Venugopalan | Multiparticle collectivity from initial state correlations in high energy proton-nucleus collisions | PRL 120 (2018) 042002 | 1705.00745 |
| 31 | L. He et al. | Anisotropic parton escape is the dominant source of azimuthal anisotropy in transport models | PLB 753 (2016) 506 | 1502.05572 |
| 32 | CMS Collaboration | Long-range two-particle correlations of strange hadrons with charged particles in pPb and PbPb collisions at LHC energies | PLB 742 (2015) 200 | CMS-HIN-14-002 1409.3392 |
| 33 | CMS Collaboration | Elliptic flow of charm and strange hadrons in high-multiplicity pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV | PRL 121 (2018) 082301 | CMS-HIN-17-003 1804.09767 |
| 34 | J.-Y. Ollitrault and M. Luzum | Eliminating experimental bias in anisotropic-flow measurements of high-energy nuclear collisions | PRC 87 (2013) 044907 | 1209.2323 |
| 35 | A. Bilandzic, R. Snellings, and S. Voloshin | Flow analysis with cumulants: Direct calculations | PRC 83 (2011) 044913 | 1010.0233 |
| 36 | ALICE Collaboration | Anisotropic flow fluctuations of charged and identified hadrons in PbPb collisions with the ALICE detector | NP A 1005 (2021) 121997 | |
| 37 | CMS Collaboration | Probing charm quark dynamics via multiparticle correlations in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | (12, 2021). Submitted to PRLett | CMS-HIN-20-001 2112.12236 |
| 38 | CMS Collaboration | HEPData record for this analysis | link | |
| 39 | CMS Collaboration | Track impact parameter resolution for the full pseudorapidity coverage in the 2017 dataset with the CMS Phase-1 pixel detector | CDS | |
| 40 | CMS Collaboration | Description and performance of track and primary-vertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker | JINST 9 (2014) P10009 | CMS-TRK-11-001 1405.6569 |
| 41 | GEANT4 Collaboration | GEANT4--a simulation toolkit | NIMA 506 (2003) 250 | |
| 42 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS experiment at the CERN LHC | JINST 3 (2008) S08004 | CMS-00-001 |
| 43 | CMS Collaboration | The CMS trigger system | JINST 12 (2017) 01020 | CMS-TRG-12-001 1609.02366 |
| 44 | CMS Collaboration | Charged-particle nuclear modification factors in PbPb and pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | JHEP 04 (2017) 039 | CMS-HIN-15-015 1611.01664 |
| 45 | CMS Collaboration | Observation and studies of jet quenching in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 2.76 TeV | PRC 84 (2011) 024906 | CMS-HIN-10-004 1102.1957 |
| 46 | CMS Collaboration | CMS luminosity measurement using 2016 proton-nucleus collisions at nucleon-nucleon center-of-mass energy of 8.16 TeV | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-002 | CMS-PAS-LUM-17-002 |
| 47 | CMS Collaboration | Performance of the CMS Level-1 trigger in proton-proton collisions at $ \sqrt{s} = $ 13 TeV | JINST 15 (2020) P10017 | CMS-TRG-17-001 2006.10165 |
| 48 | CMS Collaboration | Multiplicity and transverse momentum dependence of two- and four-particle correlations in pPb and PbPb collisions | PLB 724 (2013) 213 | CMS-HIN-13-002 1305.0609 |
| 49 | CMS Collaboration | Particle-flow reconstruction and global event description with the CMS detector | JINST 12 (2017) P10003 | CMS-PRF-14-001 1706.04965 |
| 50 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | The anti-$ {k_{\mathrm{T}}} $ jet clustering algorithm | JHEP 04 (2008) 063 | 0802.1189 |
| 51 | M. Cacciari, G. P. Salam, and G. Soyez | FastJet user manual | EPJC 72 (2012) 1896 | 1111.6097 |
| 52 | O. Kodolova, I. Vardanian, A. Nikitenko, and A. Oulianov | The performance of the jet identification and reconstruction in heavy ions collisions with CMS detector | EPJC 50 (2007) 117 | |
| 53 | Particle Data Group, P. A. Zyla et al. | Review of particle physics | Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2020 (2020) 083C01 | |
| 54 | A. Hoecker et al. | TMVA: Toolkit for multivariate data analysis | PoS ACAT (2007) 040 | physics/0703039 |
| 55 | I. P. Lokhtin and A. M. Snigirev | A model of jet quenching in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions and high-$ {p_{\mathrm{T}}} $ hadron spectra at RHIC | EPJC 45 (2006) 211 | hep-ph/0506189 |
| 56 | CMS Collaboration | Multiplicity and rapidity dependence of strange hadron production in pp, pPb, and PbPb collisions at the LHC | PLB 768 (2017) 103 | CMS-HIN-15-006 1605.06699 |
| 57 | A. Bilandzic et al. | Generic framework for anisotropic flow analyses with multiparticle azimuthal correlations | PRC 89 (2014) 064904 | 1312.3572 |
| 58 | CMS Collaboration | Pseudorapidity and transverse momentum dependence of flow harmonics in pPb and PbPb collisions | PRC 98 (2018) 044902 | CMS-HIN-15-008 1710.07864 |
| 59 | CMS Collaboration | Azimuthal anisotropy of charged particles with transverse momentum up to 100 $ GeV/$c in PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | PLB 776 (2018) 195 | CMS-HIN-15-014 1702.00630 |
| 60 | CMS Collaboration | Multiparticle correlation studies in pPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 8.16 TeV | PRC 101 (2020) 014912 | CMS-HIN-17-004 1904.11519 |
| 61 | N. Borghini, P. M. Dinh, and J.-Y. Ollitrault | Flow analysis from multiparticle azimuthal correlations | PRC 64 (2001) 054901 | nucl-th/0105040 |
| 62 | J. Jia, M. Zhou, and A. Trzupek | Revealing long-range multiparticle collectivity in small collision systems via subevent cumulants | PRC 96 (2017) 034906 | 1701.03830 |
| 63 | CMS Collaboration | Comparing transverse momentum balance of b jet pairs in pp and PbPb collisions at $ {\sqrt {\smash [b]{s_{_{\mathrm {NN}}}}}} = $ 5.02 TeV | JHEP 03 (2018) 181 | CMS-HIN-16-005 1802.00707 |
| 64 | W. Zhao, H.-j. Xu, and H. Song | Collective flow in 2.76 TeV and 5.02 A TeV Pb+Pb collisions | EPJC 77 (2017) 645 | 1703.10792 |
| 65 | H.-j. Xu, Z. Li, and H. Song | High-order flow harmonics of identified hadrons in 2.76A TeV PbPb collisions | PRC 93 (2016) 064905 | 1602.02029 |
| 66 | CMS Collaboration | Evidence for transverse momentum and pseudorapidity dependent event plane fluctuations in PbPb and pPb collisions | PRC 92 (2015) 034911 | CMS-HIN-14-012 1503.01692 |
| 67 | PHOBOS Collaboration | Importance of correlations and fluctuations on the initial source eccentricity in high-energy nucleus-nucleus collisions | PRC 77 (2008) 014906 | 0711.3724 |
| 68 | J.-Y. Ollitrault, A. M. Poskanzer, and S. A. Voloshin | Effect of flow fluctuations and nonflow on elliptic flow methods | PRC 80 (2009) 014904 | 0904.2315 |
| 69 | J. S. Moreland, J. E. Bernhard, and S. A. Bass | Alternative ansatz to wounded nucleon and binary collision scaling in high-energy nuclear collisions | PRC 92 (2015) 011901 | 1412.4708 |

|
Compact Muon Solenoid LHC, CERN |

|
|
|
|
|

|